What is Rational use of Medicines?
“Rational use of medicines” means prescribing right medicines, in adequate dose for the sufficient duration and appropriate to the clinical needs of the patient at lowest cost’. “तर्कसंगत उपयोग (Rational use)” का अर्थ है, पर्याप्त अवधि के लिए पर्याप्त खुराक में और न्यूनतम लागत पर रोगी की नैदानिक आवश्यकताओं के लिए उपयुक्त दवाओं को निर्धारित करना।
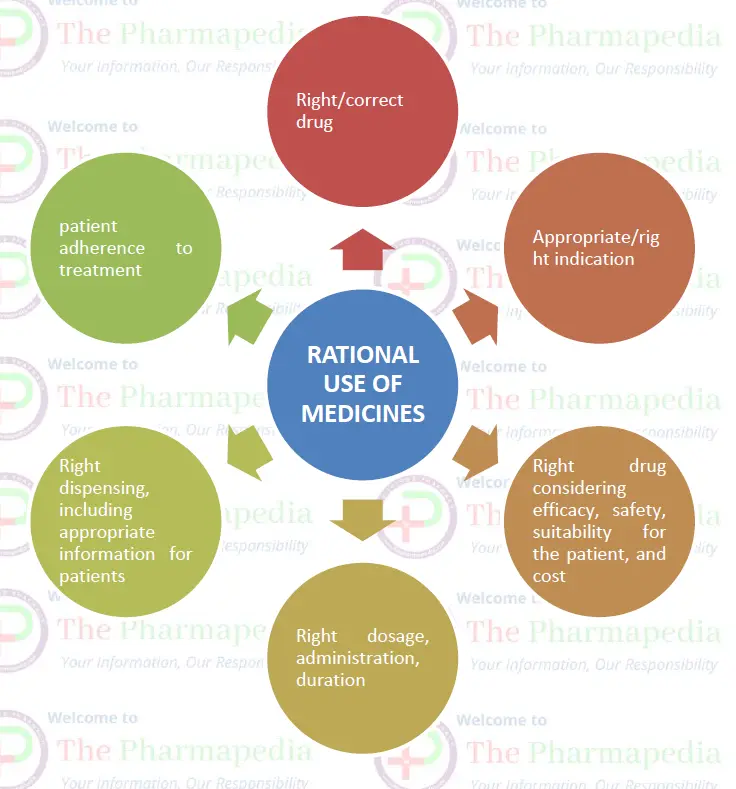
Rational Use of Medicines requires that patients receive medications appropriate to their clinical needs, in doses that meet their own individual requirements, for an adequate period of time, and at affordable cost to them and the community (WHO, 1985).The Rational Use of Medicines results into a more effective treatment at an affordable cost. दवाओं के तर्कसंगत उपयोग (रैशनल यूज़ ) का परिणाम है: मरीज/कम्युनिटी को सस्ती कीमत पर प्रभावी उपचार मिलना।
Rational drug use implies correct drug, appropriate indication and selection with respect to efficacy, safety, suitability for the patient and cost.
Three tools have been identified to implement Rational Use of Medicines effectively. These include
- Essential Medicines List
- Standard Treatment Guidelines and
- Drug Formulary
Rational Approach To Therapeutics
Medicines should only be prescribed when necessary. Bad prescribing habits lead to ineffective and unsafe treatment, exacerbation or prolongation of illness, distress and harm to the patient, and higher cost.
The following steps will help to remind prescribers/physician of the rational approach to therapeutics.
1. Define the patient’s problem-
Whenever possible, making the right diagnosis is based on integrating many pieces of information: the complaint as described by the patient; a detailed history; physical examination; laboratory tests; X-rays and other investigations. This will help in rational prescribing, always bearing in mind that disease are evolutionary process.
2. Specify the therapeutic objective-
Doctors must clearly state their therapeutic objectives based on the pathophysiology underlying the clinical situation. Very often physicians must select more than one therapeutic goal for each patient.
3. Selecting therapeutic strategies-
The selected strategy should be discussed with the patient. The selected treatment can be non-pharmacological and/or pharmacological; it also needs to take into account the total cost of all therapeutic options.
a. Non-pharmacological treatment–
The patient does not always need a medicine for treatment of the condition. Very often, health problems can be resolved by a change in life style, dietary habits, use of physiotherapy or exercise, provision of adequate psychological support and other non- pharmacological treatments; they have the same importance as a prescription drug and instructions must be written, explained and monitored in the same way.
b. Pharmacological treatment-
Selecting the correct group of drugs
Knowledge about the pathophysiology involved in the clinical situation of each patient and the pharmacodynamics of the chosen group of drugs, are two of the fundamental principles for rational therapeutics.
Selecting the drug from the chosen group
The selection process must consider benefit/risk/cost information. This step is based on evidence about maximal clinical benefits of the drug for a given indication (efficacy) with minimum production of adverse effects (safety). It must be remembered that each drug has adverse effects and it is estimated that up to 10% of hospital admissions in industrialized countries are due to adverse effects. Not all drug-induced injury can be prevented but much of it is caused by inappropriate selection of drugs. In cost comparisons between drugs, the cost of total treatment and not only the unit cost of the drug must be considered.
Verifying the suitability of the chosen pharmaceutical treatment of each patient
The prescriber must check suitability of the chosen active substance, its dosage form, dosage schedule and duration of treatment are suitable for each patient. Drug treatment should be individualized to the needs of each patient.
Prescription writing
The prescription is the link between the prescriber, the pharmacist (or dispenser) and the patient so it is important for successful management of presenting medical condition. The item is covered in more detail in the following section.
Giving information, instructions and warnings
This step is important to ensure patient adherence and is covered in detail in the following section
Monitoring treatment
Evaluation of the follow up and the outcome of treatment provides information whether the patient’s problem is solved or to reformulate, if necessary. This step gives rise to important information about the effects and adverse effects of medicines, contributing to the evidence of knowledge, necessary to promote the rational use of drugs.
Why does irrational use continue?
Very few countries regularly monitor drug use and implement effective nation-wide interventions. Most of developing countries do not monitor drug use because of
- they have insufficient funds or personnel
- they lack of awareness about the funds wasted through irrational use
- there is insufficient knowledge of concerning the cost-effectiveness of interventions
Also Read…
Standard Treatment Guidelines | Pharmacotherapeutics
Essential Medicines List (EML)-Pharmacotherapeutics
Join Our WhatsApp Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to Download Free Books & Notes, Previous papers for D.Pharm, B.Pharm, M.Pharm, Drug Inspector & GPAT……….

Comments are closed