National health mission/राष्ट्रीय स्वास्थ्य मिशन (NHM)
National health mission (NHM) was launched by the government of India in 2013 subsuming the National Rural Health Mission (Launched in 2005) and National Urban Health Mission (Launched in 2013).राष्ट्रीय ग्रामीण स्वास्थ्य मिशन (2005 में लॉन्च) और राष्ट्रीय शहरी स्वास्थ्य मिशन (2013 में लॉन्च) को समाहित करते हुए 2013 में भारत सरकार द्वारा राष्ट्रीय स्वास्थ्य मिशन (NHM) लॉन्च किया गया था|
Due to the poor knowledge and sources (mainly in rural area) some people are not able to take the government facilities. For releasing this problem government introduce the new programs (NHM one of them) to full fill the requirement and improve the health of the needy person.
The main programmatic components include Health system strengthening in rural and urban areas, Reproductive Maternal- Neonatal-Child and Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A) and Communicable and Non -Communicable Diseases.
Components of NHM
- Maternal health, Neonatal-child health, Reproductive health (RMNCH+A)
- Health Systems Strengthening (स्वास्थ्य प्रणाली को सुदृढ़ करना)
- Communicable diesease Control Programmes
- Non -Communicable Diseases Control Programmes
- Infrastructure Maintenance
Goals of NHM
- 1. Reduce MMR (Maternal Mortality Rate) to 1/1000 live births
- 2. Reduce IMR (Infant Mortality Rate) to 25/1000 live births
- 3. Reduce TFR (total fertility rate) to 2.1
- 4. Prevention and reduction of anaemia in women aged 15–49 years
- 5. Prevent and reduce mortality & morbidity from communicable, non- communicable; injuries and emerging diseases
- 6. Reduce household out-of-pocket expenditure on total health care expenditure
- 7. Reduce annual incidence and mortality from Tuberculosis by half
- 8. Reduce the prevalence of Leprosy to <1/10000 population and incidence to zero in all districts
- 9. Annual Malaria Incidence to be <1/1000
- 10. Less than 1 percent microfilaria prevalence in all districts
- 11. Kala-azar Elimination by 2015, <1 case per 10000 population in all blocks
AIM OF NHM
- Improve the health conditions of the people.
- Awareness about Adolescence and bad habits.
- Prevention against disease.
- Improve hygienic condition.
- Aware about the natural sources.
- Maintenance of population growth.
- Provide the all facilities to required persons
Achievements of NHM
- Improvement in Health Indicators:
- In the 15 years of implementation, the NHM has enabled achievement of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) for health.
- The MDGs have been superseded by the Sustainable Development Goals.
- It has also led to significant improvements in maternal, new-born, and child health indicators, particularly for maternal mortality ratio, infant and under five mortality rates, wherein the rates of decline in India are much higher than the global averages and these declines have accelerated during the period of implementation of NHM.
- In the 15 years of implementation, the NHM has enabled achievement of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) for health.
- Growth in Public Health Facilities:
- NHM adopts a health system approach and targets to build a network for public health facilities with Health & Wellness Centres at the grassroot level and District Hospitals, with robust referral linkage, to offer Comprehensive primary and secondary care services to citizens.
- NHM has not only contributed to increase in the institutional capacities for service delivery but also has led to development of capacities for targeted interventions of the various National Programmes under the NHM.
- Equitable Development:
- There was also a sustained focus on the health of tribal populations, those in Left Wing Extremism areas, and the urban poor.
- A more recent effort at ensuring equity in access and use, is the Aspirational district initiative, in which 115 districts across 28 states, with weak social and human development indicators have been identified for allocation of additional resources and capacity enhancement to catch up with more progressive districts.
- National Ambulance Services:
- At the time of launch of NRHM (2005), ambulance networks were non-existent.
- So far, 20,990 Emergency Response Service Vehicles are operational under NRHM.
- Besides 5,499 patient transport vehicles are also deployed, particularly for providing “free pickup and drop back” facilities to pregnant women and sick infants.
- Human Resource Augmentation:
- NHM supports states for engaging service delivery HR such as doctors, nurses and health workers and also implements the world’s largest community health volunteer programme through the Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs).
- More than 10 lakhs ASHAs and ASHA facilitators are engaged under NHM.
- NHM has also supported states to acquire staff with skills in public health, finance, planning and management to plan and implement interventions, freeing up clinical staff to deliver health services.
- NHM supports states for engaging service delivery HR such as doctors, nurses and health workers and also implements the world’s largest community health volunteer programme through the Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHAs).
- Health Sector Reforms:
- NHM enabled the design and implementation of reforms specifically related to Governance, Procurement and Technology.
- Addressing high Out-of-Pocket Expenditure (OOPE):
- Recognising the need for reducing the current high levels of OOPE, and that, almost 70% of the OOPE is on account of drugs and diagnostics, the Free Drugs and Free Diagnostics Services Initiatives have been implemented under the NHM.
- The National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM) and the Essential Diagnostics Lists have been notified and are periodically updated to include more essential drugs based on new initiatives undertaken.
On the basis of development NHM are divided into two parts—
- National Rural Health Mission (राष्ट्रीय ग्रामीण स्वास्थ्य मिशन)
- National Urban Health Mission (राष्ट्रीय शहरी स्वास्थ्य मिशन)
1. National Rural Health Mission (NRHM)
The National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) was launched on 12th April 2005, to provide accessible, affordable and quality health care to the rural population.
NHRM was launched to address the health needs of the undeserved rural population especially women, children, vulnerable sections of the society and to provide affordable, accessible and quality healthcare.
In NRHM Ayush (Ayurveda, Yoga, Siddhi, and Unani and Homeopathic) for promotion of healthy life style.
Main approaches of NHRM
- INNOVATION IN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
- COMMUNITIZE
- INNOVATION IN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
- FLEXIBLE FINANCING
- MONITOR PROGRESS AGAINST STANDARDS
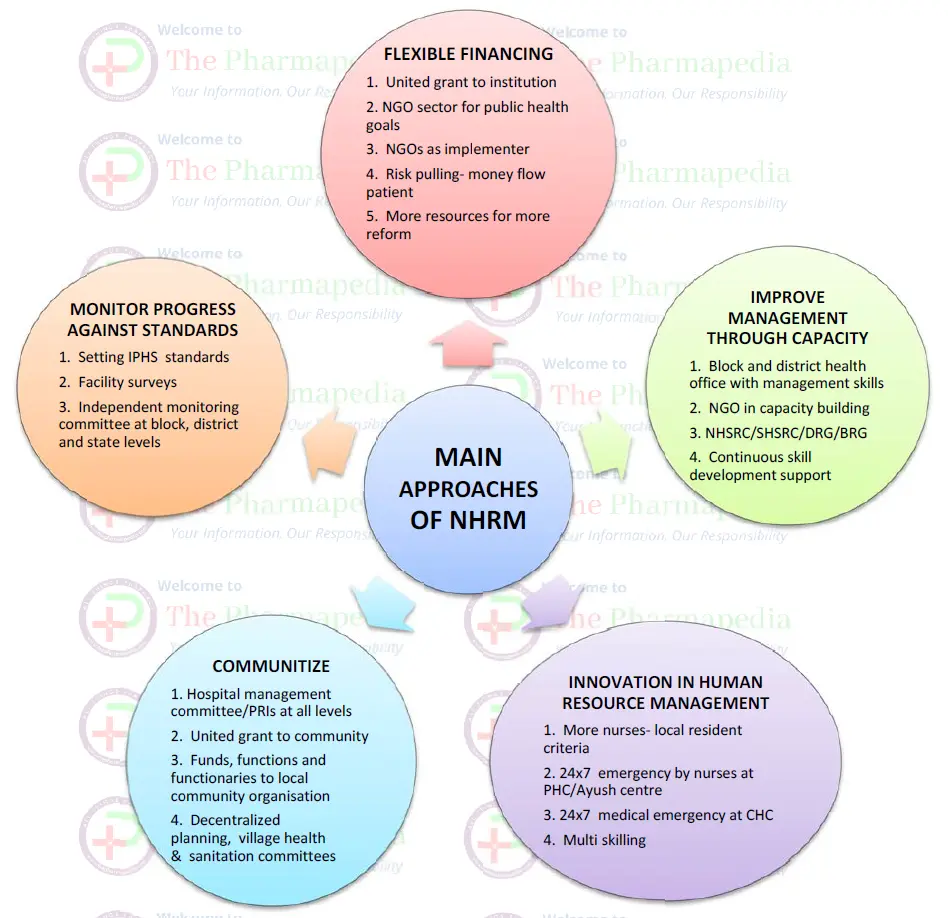
Aim of NRHM
- To provide accessible, affordable, accountable, effective and reliable primary health care in the rural through the creation of accredited social health activist (ASHA)
- To improve access of rural people, especially poor women and children.
Objectives of the Mission
- Reduction in child and maternal mortality
- Universal access to public services for food and nutrition, sanitation and hygiene and
- Universal access to public health care services with emphasis on services addressing women’s and children’s health and universal immunization
- Prevention and control of communicable and non-communicable diseases, including locally endemic diseases.
- Access to integrated comprehensive primary health care.
- Population stabilization, gender and demographic balance.
- Revitalize local health traditions & mainstream AYUSH.
- Promotion of healthy life styles.
Plan of action of NRHM
- Accredited social health activists (ASHAs)
- Strengthening sub centres
- Strengthening primary health centres
- Sanitation and hygiene
- Strengthening disease control program
- Public and private partnership fpr improving public health
2. National Urban Health Mission (NUHM)
- The National Urban Health Mission (NUHM) has been approved by the Cabinet on 1st May 2013.
- NUHM has been launched to meet health care needs of the urban population.
- NUHM focus on urban poor, by providing to them essential primary health care services and reducing their out of pocket expenses for treatment. This will be achieved by strengthening the existing health care service delivery system, targeting the people living in slums and converging with various schemes relating to wider determinants of health like drinking water, sanitation, school education.
- NUHM would cover all State capitals, district headquarters and cities/towns with a population of more than 50000.
- It primarily focus on slum dwellers and other marginalized groups like rickshaw pullers, street vendors, railway and bus station coolies, homeless people, street children, construction site workers.
- The centre-state funding pattern will be 75:25 for all the States except North-Eastern states including Sikkim and other special category states of Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand, for whom the centre-state funding pattern will be 90:10.
Goals of NUHM:
i) Need based city specific urban health care system to meet the diverse health care needs of the urban poor and other vulnerable sections.
ii) Institutional mechanism and management systems to meet the health-related challenges of a rapidly growing urban population.
iii) Partnership with community and local bodies for a more proactive involvement in planning, implementation, and monitoring of health activities.
iv) Availability of resources for providing essential primary health care to urban poor.
v) Partnerships with NGOs, for profit and not for profit health service providers and other stakeholders.
Organization of Urban health care facility under NUHM

Urban Health Care Delivery Model

Bibliography
Join Our WhatsApp Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to Download Free Books & Notes, Previous papers for D.Pharm, B.Pharm, M.Pharm, Drug Inspector & GPAT……….
