Size reduction is a process of reduction of material to smaller pieces to coarse particles or to powder/fine powder.
Size reduction process is also known as Comminution and Grinding.
When the particle size of solids is reduced by mechanical means it is known as Milling. The size reduction operation can be divided into two major categories depending on whether the material is a solid or a liquid.
If the material is solid, the process is called grinding and cutting, if it is liquid, emulsification or atomization.
Factors Affecting Size Reduction
Pharmaceutical Industry uses a great variety of materials (chemical, animal tissues & vegetable drugs).
I. Hardness:
- Surface property of the materials
- Arbitrary scale of hardness is Mohs scale (1 to 10; from Graphite to diamond)
- 1 -3 = Soft – Finger nail
- 4 – 7 = Intermediate hard
- > 7 = Hard
- It is easy to reduce the size of soft materials as compared to hard materials.
- Harder the material more difficult to cut.
II. Toughness:
- Toughness creates more problems in size reduction than a hard. (eg. Chalk & rubber)
- Toughness encountered with particularly fibrous drug with moisture content. (eg Green twig & dry twig)
- Liq. N2 /Nitrogen = (-100 to -150 oC ) is used for such materials= rubber act as glass at low temperature.
- Use of Liq. N2 /Nitrogen
- Suitable for Thermolabile substance
- No lose of volatile substance
- No oxidation
- No explosion
- The crude drugs having fibrous nature containing more moisture content are more difficult for size reduction than hard but brittle substances.
- Drawback:- Metal of machine at low temperature become brittle & lubricant become solidify.
III. Stickiness:
- The gummy materials such as resins tend to adhere to grinding surfaces or sieves of the mill and produce a lot of problems during operation. In such cases complete drying of materials is useful.
- Heat generated during milling process + Gummy & resinous substance may adhere to during milling grinding surface meshes of screen become choked.
- Completed dryness & Addition of inert substance – used to overcome stickiness
IV. Abrasiveness
It is property of hard materials particularly those of mineral origin.
During Grinding of Abrasive substance, final powder becomes contaminated with metal worm from the grinding mill.
V. Material Structure:
- Materials with a special structure such as plant materials and minerals with weakness lines produce fibers and flakes during operation and produce problems.
- Homogeneous
- Mineral origin
- Cellular & fibrous particles
VI. Moisture Content:
- Moisture content influences material properties like hardness, toughness or stickiness.
- The moisture content of material influence many properties like hardness, toughness, stickiness etc.. Usually 5% moisture in dry grinding and 50% moisture in wet grinding is considered good for size reduction.
VII. Softening Temperature:
- Size reduction/milling process generate a heat which cause substance to soften [specially with fatty or waxy materials like stearic acid, oil/ fats]
- This can be overcome by cooling the mill by
- Water jackets
- Use of liquid Nitrogen
- Passing a stream of air through equipment
VIII. Purity Required:
The grinding surfaces of mills may wear off and appear in the final product and compromise the purity of final product. This can be avoided by proper selection of mills and cleaning of mill between batches.
IX. Physiological Effect of Material:
small amount of dust of a very potent (podophyllum, hormone) may have an effect on operators. Enclosed mill must be used or wet grinding or air extraction system are desirable.
X. Ratio of feed size to product size:
Fine powder require a small feeding size.
Carry out size reduction in several stages with diff. equipment. Eg. Preliminary crushing, followed by Coarse than fine grinding
Importance/advantage of size reduction:
Improve dissolution rate
Size reduction reduces particle size and increases effective surface area which in turn increases the rate of solution which result into high dissolution rate.
Effective extraction of drug
Rate of extraction is directly proportional to Size reduction. Smaller particle size allows faster penetration of menstruum and hence fastens the extraction process.
Uniform mixing
Smaller particle size ensures effective mixing which is an essential thing for many pharmaceutical dosage forms.
Bioavailability
As particle size decreases the rate of absorption increases. Hence size reduction ensures good bioavailability e.g Griseofulvin.
Uniform Drying
Reduction in particle size increases effective surface area and fastens the process of drying.
Content uniformity
Disadvantage of size reduction
Drug degradation: Decomposition of drug can occurs due to excessive heat production during milling/size reduction process. Also increased surface area leads to drug decomposition.
Poor mixing: There is strong cohesive force between very fine particles so aggregation of particles take place. aggregation inhibits blending.
Contamination: During the milling process, there is chance of contamination of drug with mill component due to wear & tear.
Mechanism of size reduction
1) Cutting– Cutter mill
2) Compression– Roller mill
3) Impact– Hammer mill
4) Attrition– Roller Mill
5) Combined impact and attrition– Ball Mill, Fluid energy mill



1) Rotary Cutter Mill
Principle:
Size Reduction involves successive cutting the feed material with help of sharp knife.

Construction and working principle:
The equipment has two parts – one is rotor and another part is the casing. Stationary knives are fitted on the casing and rotating knives are fitted on the rotor. Feed enters through the top hopper. The rotor rotates and both stationary and rotating knives cut the material into pieces. The lower part consists of a screen, so that material is retained in the mill until sufficient degree of size reduction has been effected.
Applications:
This method is used to obtain coarse degree of size reduction of soft materials. Applied in size reduction of roots, peels or woods, prior to extraction.
2) Roller mill
Principle: Compression

Construction and working principle:
The roller mill has two cylindrical rolls of stone or metal, mounted horizontally, which are capable of rotating on their longitudinal axes. One roll is rotated directly and the other rotates freely. When material is placed above the rolls it is drawn in through the nip and the second roll is rotated by friction.
Diameter of the rolls: Few centimeter up to several meters The gap between the roll may be adjusted to control the degree of size reduction.
Applications:
Used for crushing or cracking seeds prior to extraction of fixed oils or bruising soft tissues (often after cutting) to aid solvent penetration.
3) Hammer mill
Principle: Impact

Construction and working principle:
Hammer mill consists of a stout metal casing, enclosing a central shaft to which four or more hammers are attached. These are mounted with swivel joints, so that the hammers swing out to a radial position when the shaft is rotated. The lower part of the casing consists of screen through which materials can escape, when sufficiently size reduced. The material is collected in a container placed below the screen.
- The screen can be changed according to the particle size required.
- According to the purpose of operation the hammers may be square-faced, tapered to a cutting form or have a stepped-form.
- The interior of the casing may be undulating in shape, instead of smooth circular form for better impact.
- The rotor operates at a speed of 80cycles per second.
Advantages:
(a) It is rapid in action, and is capable of grinding many different types of materials.
(b) The product can be controlled by variation of rotor speed, hammer type and size and shape of mesh.
(c) Operation is continuous.
(d) No surface moves against each other so very little problem of contamination of mill materials.
Disadvantages:
- a) High speed of operation generates heat that may affect thermolabile materials or drugs containing gum, fat or resin.
- (b) The rate of feed should be controlled otherwise the mill may be choked.
- (c) Because of high speed of operation, the hammer mill may be damaged if some foreign materials like stone, metal pieces etc. are present in the feed.
Applications: Powdering of crystals and filter cakes.
4) Attrition– Roller Mill
5) Ball Mill
Principle: Combined impact and attrition
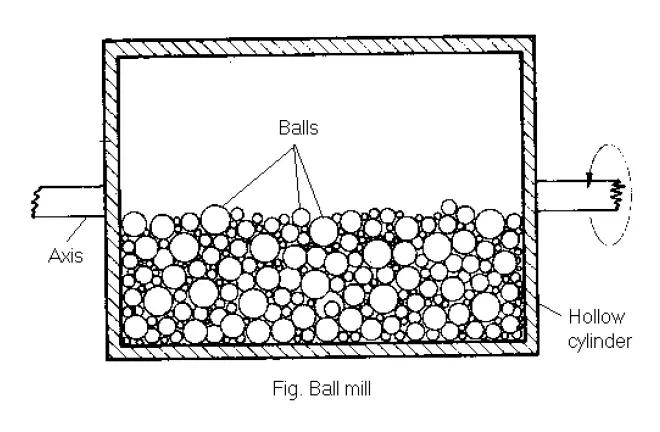
Construction
The ball mill consists of a hollow cylinder rotated on its horizontal axis. Inside the cylinder balls or pebbles are placed.
Cylinder:
- Cylinder may be made up of metal, porcelain or rubber.
- Rubber reduces the abrasion. Diameter of the cylinder ranges from 1 to 3m in pharmaceutical practice.
Balls:
- Balls occupy about 30 to 50% of the volume of the cylinder.
- Diameter of the balls depends on the feed size and diameter of the cylinder. The diameter of balls ranges from 2cm to 15cm.
- Ball of large diameter are used for crushing and small diameter’s balls are used to form the fine powder.
- Balls may be of metal, porcelain or pebbles.
Working Principle:
Larger particles are fed through an opening of the cylinder. The opening is closed. The cylinder is rotated at the critical speed of ball mill. The optimum size reduction in a ball mill depends o the following factors: Feed quantity: Too much feed will produce cushioning effect and too little feed will produce loss of efficiency of the mill.
Speed of rotation of the cylinder:
- At low speed the mass of balls will slide or roll over each other and only a negligible amount of size reduction will take place.
- At high speeds, balls will be thrown out to the wall of the cylinder due to centrifugal force and no grinding will occur.
- At 2/3rd speed at which centrifugation just occurs is called the critical speed of the ball mill. At this speed the balls are carried almost to the top of the mill and then fall in a cascade across the diameter of the mill. By this means the maximum size reduction is obtained by impact of the particles between the balls and by attrition between the balls. Generally it is 0.5 cycles per seconds (cps).

Advantages
- It is capable of grinding a wide variety of materials of differing hardness.
- It can be used in completely enclosed form, which makes it suitable for use with toxic materials.
- It can produce very fine powders.
- It is suitable both for dry and wet milling. Wet milling is required for preparation of pharmaceutical suspensions.
Disadvantages
- Wear occurs from the balls and the inside surface of the cylinder hence there is possibility of contamination of product with mill material. Abrasive materials increase wear.
- Soft or sticky materials may cause problems by caking on the sides of the mill or by holding the balls in aggregates.
- The ball mill is a very noisy machine, particularly if the cylinder is made of metal.
Applications:
Large ball mills are used to grinding ores prior to manufacture of pharmaceutical chemicals. Smaller ball mills are used for grinding of drugs or excipients or for grinding suspensions.
Variants of Ball mill
- Hardinge mill = Conical end cylinder
- Tube mill = long narrow cylinder
- Rod mill = has rods (useful for sticky materials)
- Vibration milling
6) Fluid energy mill
Principle: Combined impact and attrition

Construction:
It consists of a loop of pipe, which has a diameter of 2 to 20cm. The height of the loop may be up to 2m. Several nozzles are fitted at the bottom of the pipe. A classifier is fitted at the product collection point.
Working principle
A fluid usually air, is injected at very high pressure through nozzles at the bottom of the loop. This gives rise to a high velocity of circulation that produce turbulence. Solids are introduced into the stream through the feed inlet. As a result of high degree of turbulence, impacts and attrition occur between the particles. A classifier is fitted in the system so that only finer size particles are collected as products and the larger size particles are again sent to the stream of air for further size reduction.
The feed to the mill is previously size reduced and passed through a 100 mesh screen.
The size of the product may be 5 μm or below.
Advantages:
- The particle size of the product is smaller than that produced by any other method of size reduction.
- Expansion of gases at the nozzles lead to cooling, counteracting the usual frictional heat that can affect heat-sensitive (thermolabile) materials.
- Since the size reduction is by inter-particulate attrition there is little or no abrasion of the mill and no contamination of the product.
- For oxygen or moisture sensitive materials inert gases like nitrogen can be used instead of normal air.
- This method is used where fine powders are required like micronization of griseofulvin (an antifungal drug), antibiotics etc.
Selection of Degree of Size Reduction
| S. No. | Degree of size reduction | Typical method | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Large Pieces | Cutter or compression mills | Rhubarb |
| 2 | Coarse powders | Impact mill | |
| 3 | Fine powders | Combined Impact & attrition mills | Liquorics cascara |
| 4 | Very fine powders | Fluid energy mills | Vitamins & Antibiotics |
Join Our WhatsApp Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to Download Free Books & Notes, Previous papers for D.Pharm, B.Pharm, M.Pharm, Drug Inspector & GPAT……….

Comments are closed