Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is autoimmune disease involved IgM immune complex.
In Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) white blood cells (WBCs) identify the synovium (tissue that nourishes cartilage and bone) as non-self and initiate an inflammatory attack. WBC activation leads to stimulation of T lymphocytes (the cell-mediated immune system), which recruit and activate monocytes and macrophages. These cells secrete proinflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-1, into the synovial cavity. The release of TNF)-α and interleukin (IL) then causes
- 1) increased cellular infiltration into the endothelium due to release of histamines, kinins, and vasodilatory prostaglandins;
- 2) increased production of C-reactive protein by hepatocytes (a marker for inflammation);
- 3) increased production and release of proteolytic enzymes by chondrocytes (cells that maintain cartilage), leading to degradation of cartilage and joint space narrowing;
- 4) increased osteoclast activity (osteoclasts regulate bone breakdown), resulting in focal bone erosions and bone demineralization around joints; and
- 5) In addition to T-lymphocyte activation, B lymphocytes are also involved and produce rheumatoid factor (inflammatory marker) and other autoantibodies with the purpose of maintaining inflammation. These reactions cause progressive tissue injury, resulting in joint damage and erosions, functional disability, significant pain, and reduction in quality of life.
Briefly, Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by:-
- Joint Inflammation & pain
- Synovial Fluid proliferation
- Destruction of Articular cartilage
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis/Anti-Rheumatoid Drugs
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune multisystem disease. NSAIDs are used to provide symptomatic relief but exert no effect on the progression of the disease. Disease modifying anti-rheumatoid drugs (DMARDs) slow the progression of disease but act slowly (takes 6 weeks to 6 months).
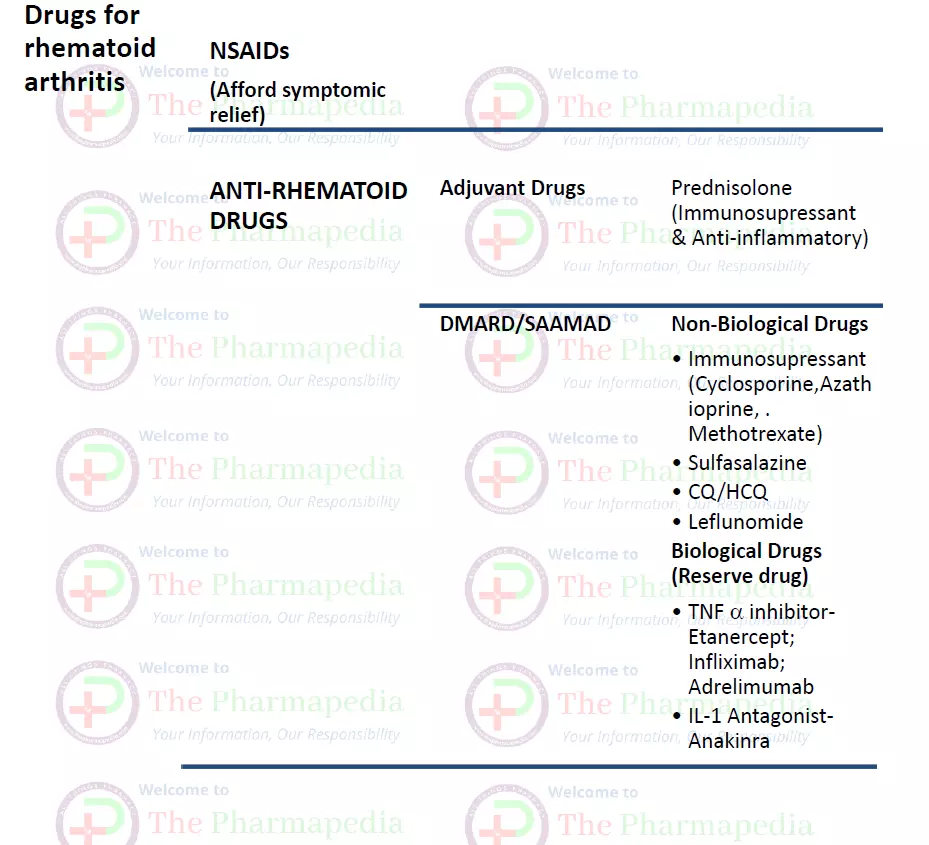
I-Anti-Rheumatoid Drugs
a) Disease modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs (DMARD)
i) Non-Biological Drugs
- Immunosuppressant
- Cyclosporine, Chorambucil & cyclophosphamide-rarely used in RA
- Azathioprine
- M/A- purine synthetase inhibitors- potent suppressant of cell mediated immunity & also suppress inflammation.
- Methotrexate
- M/A- Immunosuppressant & Anti-inflammatory action- results into inhibition of release of cytokinin’s (TNF/IL-1)
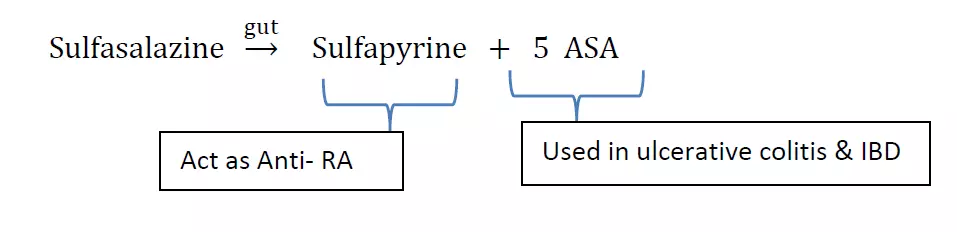
- Sulfasalazine: Sulfasalazine split off in the colon by bacterial action into Sulfapyrine & 5-ASA (5- Amino salicylic acid). Sulfapyridine suppresses disease of RA.
- Chloroquine (CQ) & Hydroxy Chloroquine (HCQ): Reduce IL-1 & inhibits B-Lymphocytes. HCQ is safe in pregnancy.
- Leflunomide
- It is Immunomodulator drug which inhibits proliferation of stimulated Lymphocytes.
- M/A- Leflunomide coverts in the body to an active metabolite which inhibits DHFRase & Pyrimidine synthesis in actively dividing cells.
- Others: Gold (Gold sodium thiomalate i.m. inj.), Auranofin (oral); Penicillamine (copper chelating agents)
ii) Biological Drugs
Several recombinant protein/monoclonal antibodies has been developed which bind & inhibit cytikines (TNF & IL-1).
=>TNF inhibitor
- Etanercept: Recombinant fusion protein of TNF receptor & Fc portion of Human IgG1
- Infliximab: Chimeral monoclonal antibody
- Adalimumab: Recombinant monoclonal anti-TNF antibody
=> IL-1 antagonist
- Anakinra
- Abatacept
- Rituximab
b) Adjuvant Drugs
- Corticosteroids: Glucocorticoids has potent Immunosuppressant & Anti-inflammatory activity.
- Prednisolone
II- NSAIDs
NSAIDs are used to provide symptomatic relief but exert no effect on the progression of the disease.
GOUT
GOUT: It is a metabolic disorder & a kind of an arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints.
Gout is characterized by Hyperuricemia, pain and inflammation due to deposition of crystal of Uric Acid in joints of our body.
Symptoms of gout include severe pain, redness and swelling in joints, often the big toe. Attacks can come suddenly, often at night.
During the breakdown of purines, Uric acid is formed. At low pH uric acid has low solubility so the blood level of uric acid is increases, results into deposition of crystals in joints, kidney & subcutaneous tissue (tophy).
Secondary Hyperuricemia: It is occur due to following conditions
- Chemotherapy/Radiation: It increase Nucleic acid metabolism – increase purine metabolism- increase Uric acid
- Drug Induced: Thiazides, pyrazinamide, ethambutol etc
Diagnosis of Gout
a. Joint Fluid Test:
Examine the urate crystals in joint fluid.
b. Blood Test:
Measure the level of uric acid in the blood.
Treatment of Gout
Two approaches can be apply for the treatment of gout.
I. First to reduce inflammation & pain associated with gout attack- NSAIDs, Colchicine, corticosteroids.
II. Second to lower the amount of uric acid in blood & to prevent gout complications by increasing uric acid excretion (uricosuric) or decreasing uric acid production (Xanthine oxidase inhibitors).
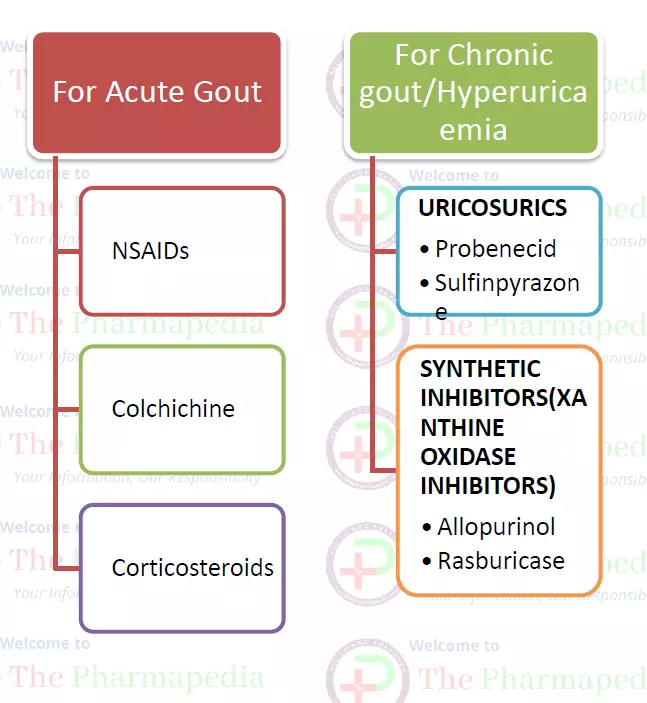
I. For Acute Gout
NSAIDs
Naproxen, Piroxicam, Diclofenac, Etoricoxib
Colchicine
Colchicine is more effective and faster acting than NSAIDs but is used rarely due to its high toxicity. It acts by inhibiting granulocyte migration into the inflamed joint, results into suppression of gouty inflammation.
Most common and dose limiting toxicity is diarrhea. It can also cause kidney damage, myopathy and bone marrow depression.
Corticosteroids: intra-articular steroids
For Chronic Gout/Hyperuricemia
Strategies to decrease uric acid in the serum are to decrease the synthesis or to increase the excretion and metabolism.
Uricosuric
These drugs increases the Excretion of Uric acid.
Probenecid, sulfinpyrazone and benzbromarone acts as competitive inhibitors of reabsorption of uric acid in proximal tubules.
Probenecid is also used along with penicillins to decrease their renal excretion.
Xanthine Oxidase inhibitors
- Drugs Decreasing Synthesis of Uric acid
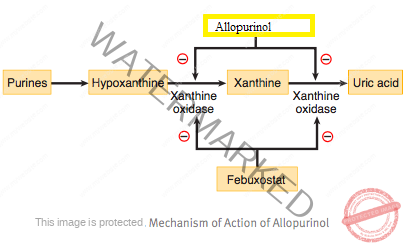
- Allopurinol (hypoxanthine analog) and recently approved drug, Febuxostat & Rasburicase (a non-purine drug) decrease the production of uric acid by inhibiting the enzyme xanthine oxidase.
MCQ QUIZ Rheumatoid Arthritis & Gout
Join Our WhatsApp Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to Download Free Books & Notes, Previous papers for D.Pharm, B.Pharm, M.Pharm, Drug Inspector & GPAT……….

Comments are closed