What is Emulsion
An Emulsion is a thermodynamically unstable system consisting of two immiscible liquid phases, one of which is dispersed/ distributed as a globules/droplet size of 0.1-100 μm (internal or dispersed phase) in the other Liquid medium(External/ continuous phase) stabilized by a third substance called an emulsifying agent.
The diameter of the dispersed phase globules is generally in the range of about 0.1 to 10 μm, although it can be as small as 0.01 μm or as large as 100 μm. It is a Biphasic Liquid Dosage Form.
The process of formation of an emulsion is termed emulsification.
The two well known examples of emulsions are:
1) Milk in which the particles of the liquid fat are dispersed in water.
2) Cod liver oil emulsion in which water is dispersed in the oil.
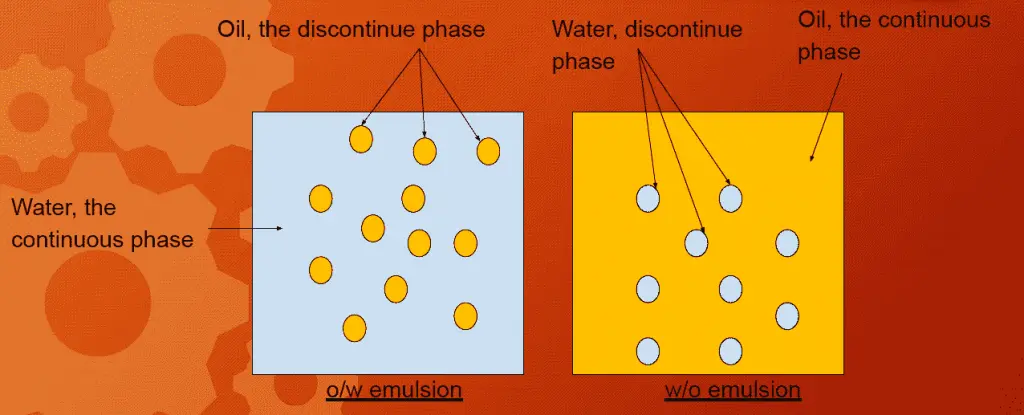
- For Pharmaceutical emulsion, globules size is 0.1 – 10 μ.
- globules/ droplets/ dispersed phase ⇒ Known as internal/ discontinue phase
- dispersion medium ⇒ known as external phase/ continuous phase
Also Read…

Comments are closed