- Haematinics are the agent required for the formation of blood and treatment of anaemia. Main haematinics include iron, folic acid and vitamin B12. Other substances like copper paradoxine are also required in small quantity for the formation of blood.
- Liver, egg yolk, beans and dry fruits are good source of iron where is milk and its products are poor sources of iron.
- Iron is an Essential body constituent that is present in the body as Hemoglobin. Hemoglobin contains a porphyrin ring & each molecule of Hemoglobin has 4 Iron-containing haeme residues in the Fe+2 form.
- Loss of 100 mL blood (15 g Hb) results in loss of 50 mg element hemoglobin.
- In the human body, Iron is stored only in Ferric form (Fe+3) with Apoferritin in RE cells
- In our diet, Iron is present in the Ferric form (Fe+3) which is reduced to Ferrous Fe+2 form and Ferrous form is absorbed in our Intestine.
Note:-
- Absorption of haem iron is better as compared to Inorganic Iron but Haem iron is a smaller fraction of dietary iron & major part of dietary iron is inorganic & in the ferric form (Fe+3).
- Hepcidin is a liver-derived peptide hormone, which is the master regulator of iron metabolism.
- Storage of Iron as Fe3+ + Apoferritin- form Ferritin (since free iron is highly toxic for the body)
- The two most common iron states are the divalent ferrous (Fe2+) and the trivalent ferric (Fe3+).
- Within the human body, iron is required as a cofactor for many haemoproteins and non-haem iron-containing proteins. Haemoproteins include haemoglobin and myoglobin that are responsible for oxygen binding and transport, catalase and peroxidase enzymes, which take part in oxygen metabolism, and cytochromes, which are involved in electron transport and mitochondrial respiration.
- Storage of Iron in the body as Ferritin in RE (liver, spleen & bone marrow), mucosal cell of intestine While transport of Iron in the form of Transferrin to the marrow for haemoglobin production.
- In the Deficiency of Iron = No. of Transferrin (Tf) Receptor increases
Excretion of Iron: Exfoliation of g.i. mucosal cells and destruction of RBCs-Bile = Lost in Faeces & Very little excretion in urine & sweat
Anemia
- Anemias are a group of diseases characterized by a decrease in hemoglobin (Hb) or red blood cells (RBCs), resulting in the decreased oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
- Haemolytic Anaemia – Destruction of RBCs
- Aplastic/Hypoplastic anemia – Due to Bone marrow depression & Erythro. deficiency
- Microcytic hypochromic anemia –Due to Iron deficiency
Types of Anemia
Anemias may occur due to following two reason
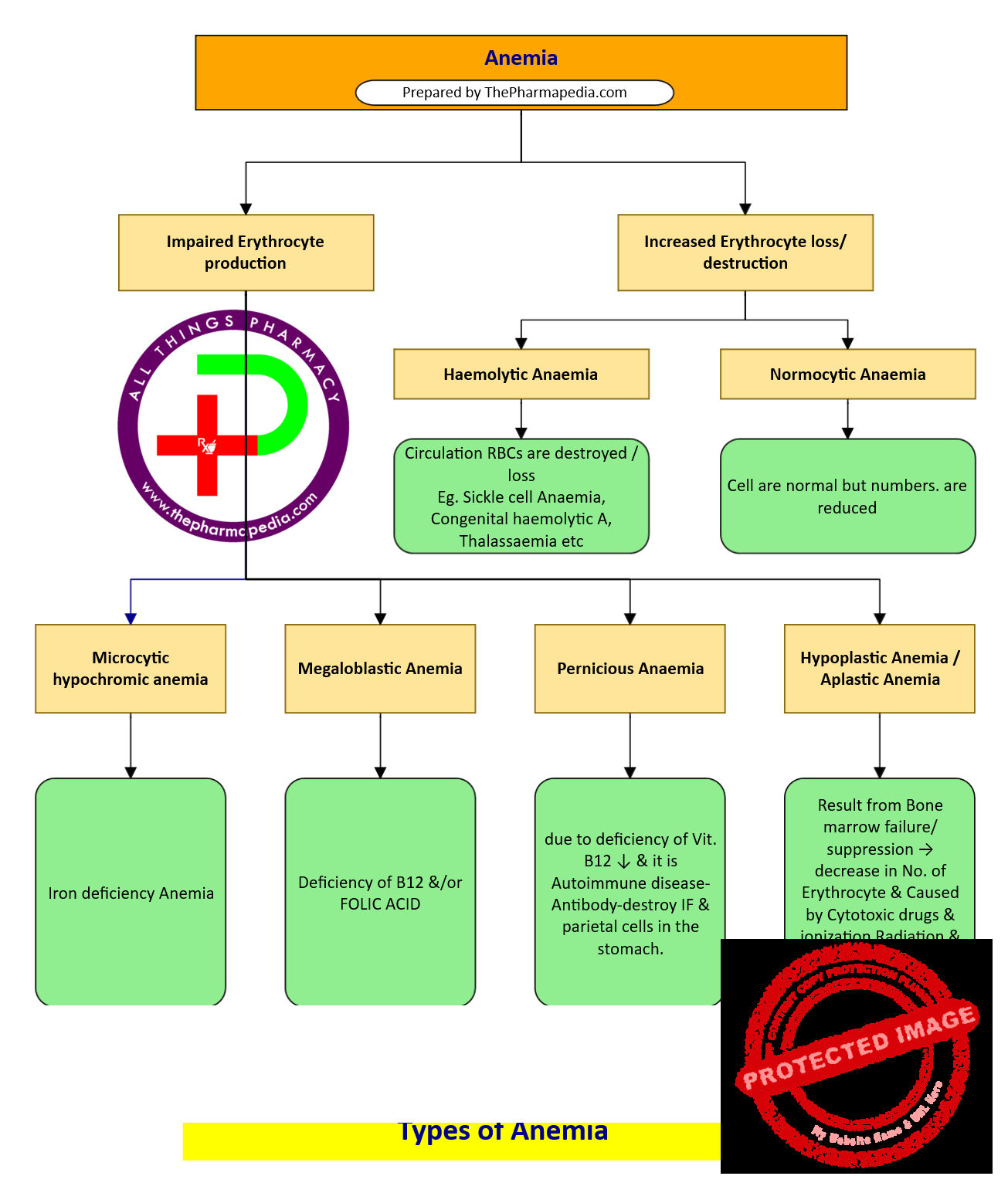
For RBCs maturation, Both Vit B12 & Folic acid are required.
IRON PREPARATION/ Drug used for Hematincs
| Oral Drugs | Parenteral / Injectable Preparations |
|---|---|
| Ferrous fumarate (33% element iron) Ferrous Gluconate(12% element iron) Ferrous sulphate (20% element iron) Iron ammonium citrate Colloidal ferric hydroxide Carbonyl iron (100% element iron)Ferrous succinate Iron choline citrate Iron calcium complex Ferric ammonium citrate Ferrous Aminoate Ferric glycerophosphate Ferric hydroxyl poly maltose Pharmacokinetics: Iron is absorbed in the stomach (acidic conditions favor more Iron absorption& duodenum Factor facilitating Iron Absorption 1. Acid = Favor dissolution & Reduction of ferric iron into the ferrous iron 2. Reducing agents: Ascorbic acid, Amino acids containing – SH Radical Reduces Fe3+ & Favor absorbable complex 3. Meat: Increase HCL secretion & meat is rich source of Heme Iron 4. Alkalies, phosphates, phytates & Tetracycline decrease Iron absorption | 1. Iron dextran Inj. 2. Iron sorbital 3. Ferrous sucrose – I.V. 4. Ferric carboxy maltose – I.V. Pharmacokinetics: Iron dextran: Macrophase phagocytizes iron dextran & release iron from Iron dextran molecules. Iron Sucrose: Specific exchange mechanism transfer Iron to Transferrin. |
| Adverse effects: -GI disturbances caused by local irritation -Abdominal pain -Dark stool -Constipation | Adverse Effect: Fetal hypersensitivity &Anaphylactoid reaction may occurs. Overdose causes Iron toxicity that can be reversed by Antidote Desferoxamine. |
| Iron Dextran | Iron Sorbital |
|---|---|
| -Can be administered by both IV & IM route | -Can be administered by only IM route |
| – Not excreted in urine | – 30 % excreted in urine |
| -Absorbed through Lymphatics | – Absorbed directly in the circulation |
Treatment of Iron Poisoning
- Antidote for acute Poisoning – Desferoxamine Inj
- Alternative – DTPA (Diethylene triamine penta acetic acid) or Calcium EDTA
- Induce vomiting or gastric lavage with NaHCO3 solution to render iron insoluble & retard absorption of iron
- Egg yolk & Milk orally – Iron complex
- Activated charcoal does not absorb iron
- BAL (British Antilecosite / Dimercaprol) – contraindicates because iron chelating complex is also toxic
Important Key point-Hematinics
Maturation factors for red blood cells/ RBC
- Maturation factors for red blood cells – vit B12 & folic acid.
Vitamin B12
- Vit. B12 :- It is synthesized in nature only by microorganisms. Plants & animals acquire it from Microorganism.
- Vit B12 is a Cobalt (Co) containing compounds [Cyanocabalamine & hydroxocabalamine diet]
- commercial source of vit B12 – Streptomyces griseus by product of streptomycin industry.
Metabolic Function of vit B12:-
- Essential for the conversion of homocysteine to methionine. Methionine is required for ‘one carbon’ transfer reaction in the synthesis of THFA (Tetrahydrofolic acid), Purine & Pyrimidine
- Metabolism of propionic acid metabolism (links carbohydrate & lipid metabolism) synthesis of phospholipids & myelin (Neurological damage).
Manifestations of Deficiency of Vit. B12 :-
- Megaloblastic Anaemia
- Damage to Epithelial structures
- Neurological – degeneration of spinal cord, peripheral neuritis, paresthesias, depressed stretch reflexes, poor memory.
Preparation of vit. B12–
- Cyanocobalamin
- Hydroxocobalamin
- Methylcobalamin
Folic acid (FA)
- Folic acid = Pteridine + para amino benzoic acid (PABA) + glutamic acid
- Folic acid is inactive as such. It is reduced to the co enzyme in two steps.

- Metabolic Functions of Folic acid :- Involve in one carbon transfer reactions.
- Conversion of homocysteine to methionine, serine to glycine
- Generation of thymidylate, purine synthesis (de novo purine synthesis)
- Manifestations of Deficiency of Folic acid:-
- Megaloblastic Anaemia, epithelial damage, neural tube defects including spina bifida in the offspring due to material folate deficiency, wt. loss & sterility.
- Use of Folic acid:-
- Megaloblastic Anaemias
- Methotrexate toxicity – Folinic acid [Leuco vorin, citro vorum factor, 5-formyl-THFA] is an active coenzyme form which does not need to be reduced by DHFRase before it can act. Since methotrexate is DHFRase inhibitor & its toxicity is not counteracted by Folic acid. It antagonized by folinic acid.
Hematopoietic growth factors
Apart from nutritional agents certain endogenous substances are required for proper hematopoiesis the substance are known as a growth factors.
The growth factor for RBC is erythropoietin which is secreted from the kidney and helps in the formation of red blood cells. Recombinant human erythropoietin (epoetin) is mainly useful for anemia due to chronic renal failure and also due to bone marrow suppression drug-like anticancer drug.
Peginesatide: It is a new drug called erythropoiesis stimulating agent. IT act by stimulating erythropoietin receptor. it is used for treatment of anaemia due to chronic renal failure in patient on dialysis.
Vitamin B12 is absorbed in the terminal ileum where is Iron is absorbed in Duodenum.

Comments are closed