Drying is final removal of liquid from solid by vaporization using heat by Dryers.
Drying can be defined as an process in which the liquid, generally water, present in a wet solid is removed by application of heat and finally a liquid free solid product is obtained.
Drying process is used mostly in industrial operations to remove moisture from a wet solid.
There are two approaches to liquid from the materials.
a). Thermal techniques– involves the application of heat.
b). Nonthermal drying processes- such as squeezing wetted sponge, adsorption by desiccant (desiccation) and extraction are also used. For example: Organic liquids or gases are dried by passing them through bed of silica gel or activated alumina which act as adsorbents.
The term evaporation is different from drying.
Difference between Drying & Evaporation
Drying
- Dry solid product is obtained
- Water is removed at the temperature below the boiling point of water
- Carrier gases such as air is used to remove water
- Small amount of water removed from solid
Evaporation
- Final product is either concentrated solution, suspension or wet slurry.
- Here water is removed at its boiling points
- No gas is used
- It include removal of large amount of water
Application of Drying
- 1. If the bulk drug ingredients are not stable in liquid or frozen form, lyophilization is necessary. Lyophilization enables longer shelf life and makes easier transport of the product.
- 2. For manufacturing of bulk drug or for large scale production of synthetic drugs, drying is essential to get free flowing materials. For example. Dried aluminium hydroxide, spray dried lactose.
- 3. It is necessary to dry fresh plants such as belladonna leaves, nux vomica, etc., before subjecting them to size reduction.
- 4. Drying is necessary to avoid deterioration of crude drugs of animal & vegetable origin, synthetic & semi synthetic drugs, aspirin & penicillin’s tablets that undergo chemical decomposition process.
- 5. Drying is necessary to avoid deterioration of blood products, skin & tissue that undergo microbial decomposition. They are dried by special process to maintain their shelf life for longer period of time.
- 6. During production of tablets, granules are dried to improve flow property as well as compression.
- 7. Viscous and sticky material are dried to improve flow property.
- 8. Some material such as milk, coffee extract are dried to convert them into instant soluble power form.
- 9. Drying is necessary to make material light weight.
- 10. Removal of moisture significantly decreases rate of chemical reactions, chances of microbial attack or enzymatic actions and thus improves stability.
Mechanism of Drying Process
Drying involves two process. First one, is Heat Transfer where heat is generated within the solid & flows to exterior surface. And second is Mass Transfer which involves movement of the moisture to the surface of the solid & its subsequent evaporation from the surface.
Water in wet solid mass either present in bound form or in unbound form. Moisture content of a substance that exerts a equilibrium vapor pressure lower than that of the pure liquid at same temperature is called bound water. Substances containing bound water are often called hygroscopic substances. Moisture content of a substance that exerts a equilibrium vapor pressure equal to that of the pure liquid at same temperature is called Unbound water. Thus, in a non hygroscopic material, all the liquid is unbound water. The moisture content of the solid in excess of the equilibrium moisture content is called free moisture. The moisture content is measured by ratio of weight of water in sample to weight of dry sample. It is expressed in percentage.
% Moisture content = (Weight of water in sample/Weight of dry sample) x 100
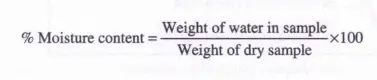
Classification of dryers
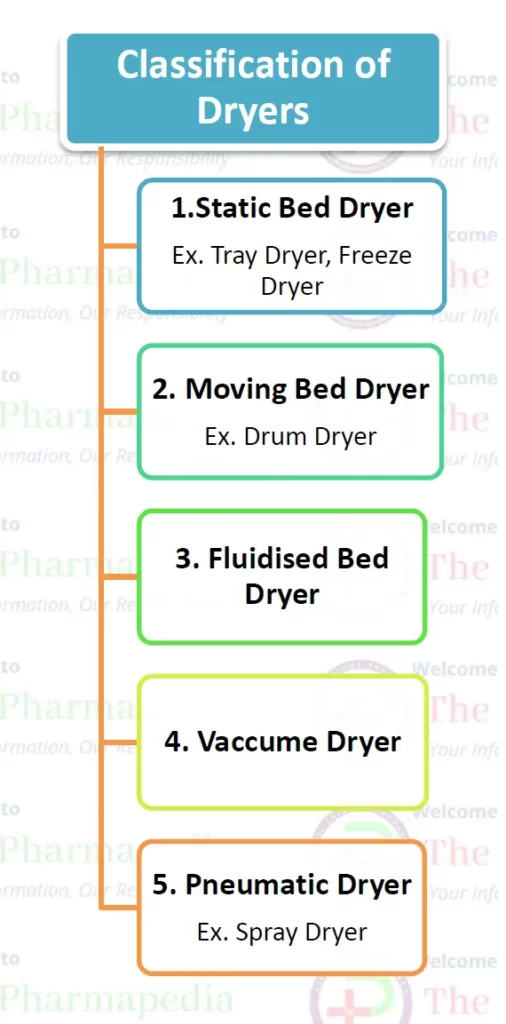
1. Static Bed Dryer
Ex. Tray Dryer, Freeze Dryer
2. Moving Bed Dryer
Ex. Drum Dryer
3. Fluidized Bed Dryer
4. Vacuum Dryer
5. Pneumatic Dryer
Ex. Spray Dryer
Note: D. Pharm syllabus includes- Drying: working of fluidized bed dryer and process of freeze drying
Also Read…
Join Our WhatsApp Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to Download Free Books & Notes, Previous papers for D.Pharm, B.Pharm, M.Pharm, Drug Inspector & GPAT……….

Comments are closed