Pharmacology of Corticosteroids
The term corticosteroid or corticoid includes natural glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids and their synthetic analogs.
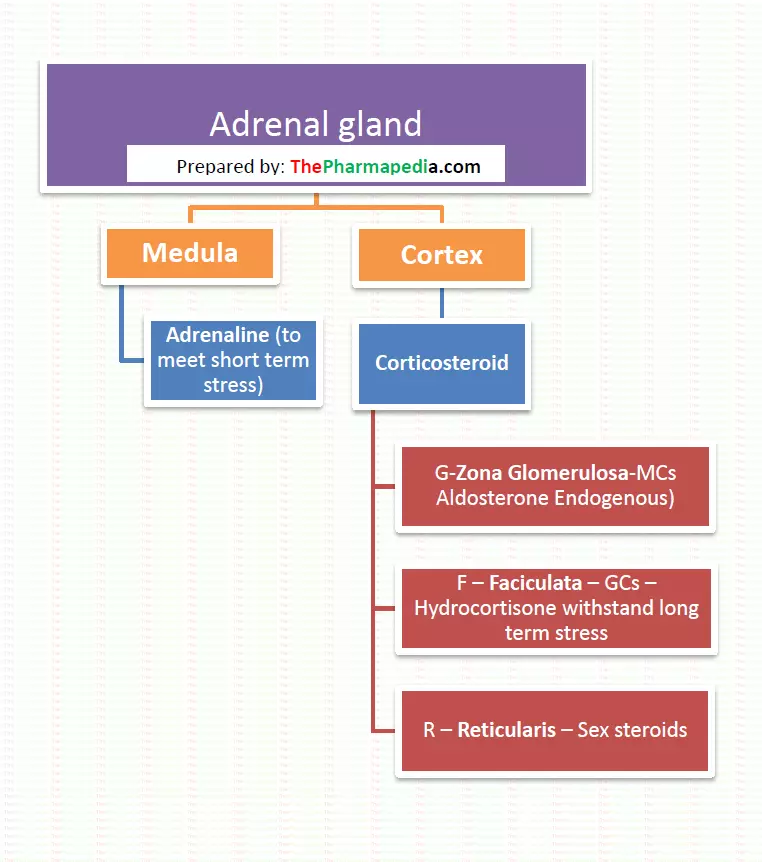
Adrenal glands have two-part: Cortex and medulla.
Context part of the adrenal gland secretes steroid hormone which includes glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids while medula part of the adrenal gland secrets sex hormones.
The adrenal cortex consists of three layers- from outside to within respectively (trick to remember-GFR)
- Zona glomerulosa
- Zona fasciculata
- Zona reticularis
Mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone) are secreted from zona glomerulosa while Zona fasciculate secrets glucocorticoids (Hydrocortisone) and zona reticularis secrets sex steroids in a small amounts.
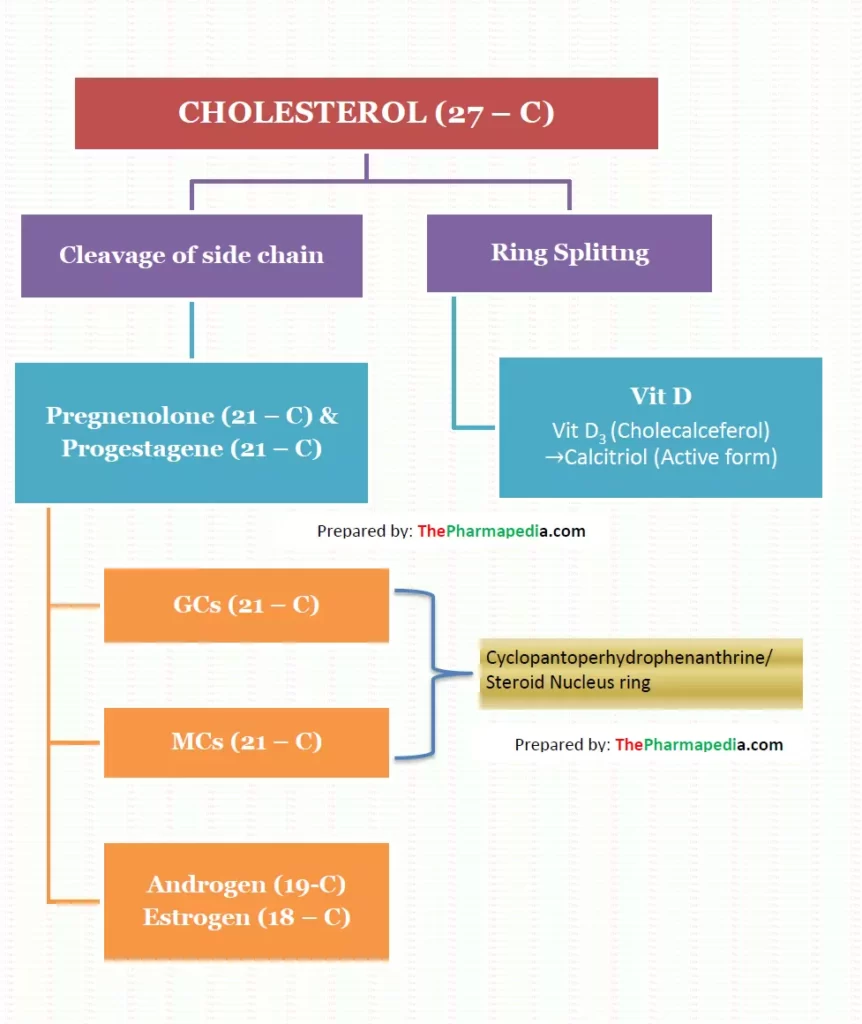
Biosynthesis of Corticoids
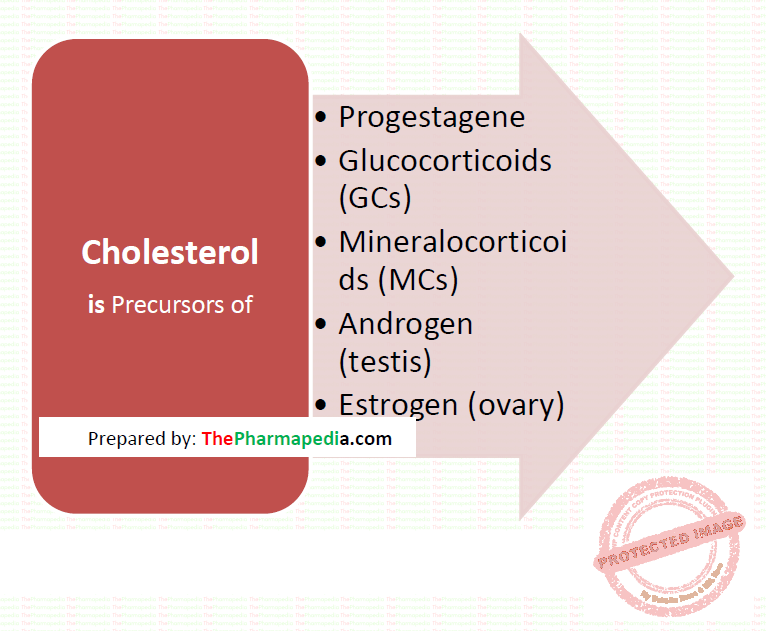
Steroid hormones in mammals are biosynthesized from cholesterol in the adrenal cortex which in in-vivo from acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) via the mevalonate pathway, under the influence of ACTH. All steroids are named as derivatives of cholestane, androstane, pregnane, or estrane.
Corticosteroids (both glucose and mineralo) are 21-carbon compound having a cyclopantenoperhydro-phenanthrene (steroid) nucleus ring. A simplified diagram of the biosynthesis pathway is presented in the figure
Conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone is the rate-limiting step in steroid hormone biosynthesis.
The normal rate of secretion of two principal corticosteroids in man are
- Hydrocortisone- 10-20 mg Daily (halh of this in the few morning hours).
- Aldosterone – 0.125 mg daily.
Action of Corticosteroids
Action of Mineralocorticoids
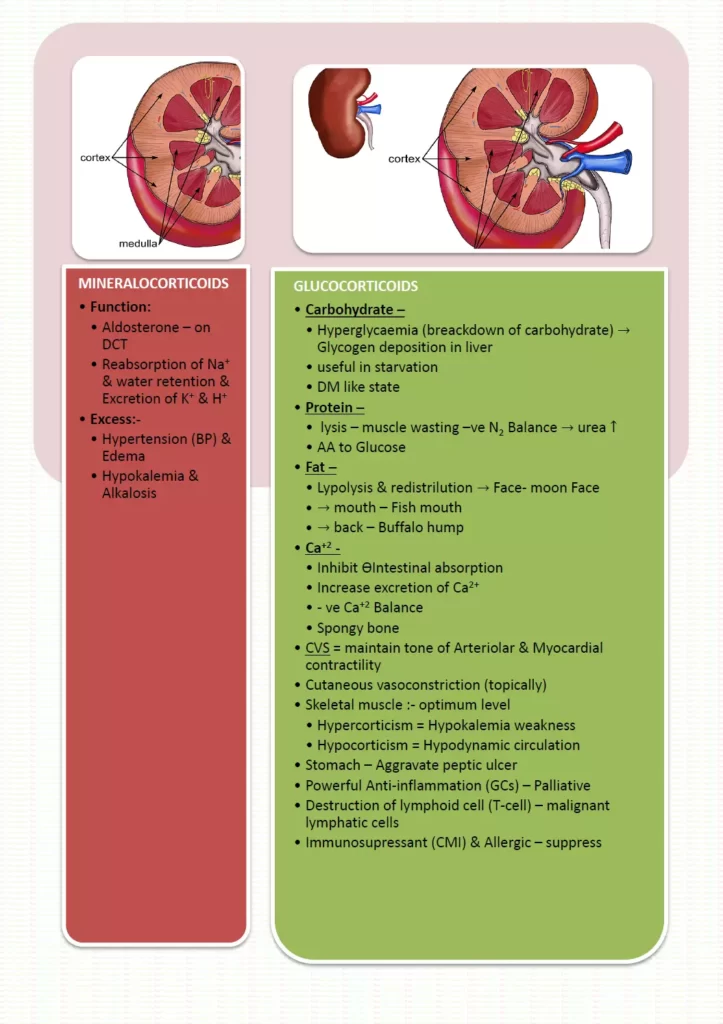
- Major endogenous mineralocorticoid is aldosterone& It acts on DCT of the kidney.
- Aldosterone causes the reabsorption of sodium. Excess of Mineralocorticoids can lead to retention of sodium and water retention which result in hypertension and edema.
- Aldosterone causes the excretion of potassium (K+)and hydrogen ions ( H+). Excess of Mineralocorticoids can lead to excretion of K+ & H+ which result in hypokalemia and alkalosis (due to loss of H+).
- Addison disease (deficiency of adrenal cortex- less Mineralocorticoids) is characterized by hyperkalemia, acidosis, and hypotension.
Action of glucocorticoid
Endogenous glucocorticoid is hydrocortisone also known as cortisol.
- Effect on metabolism
- Glucocorticoid are catabolic in nature.
- Due to catabolic nature, glucocorticoids causes breakdown of carbohydrate(hyperglycemia) breakdown of protein(muscles loss/muscle wasting), re-distribution of fat. Glucocorticoid cause deposition of fat over face (Moon face), mouth (fish mouth) & back (buffalo hump).
- Corticoids also cause negative calcium balance (by inhibiting intestinal absorption, enhancing renal excretion and causing the loss of Calcium from the bones so GCs can predispose osteoporosis.
- Effect on CVS
- Prevent the increase in the permeability of capillaries
- Effect on GIT
- GCs can aggravate peptic ulcer by increasing the secretion of HCL and pepsin in stomach.
- Effect on haemopoietic system
- GCs cause destruction of T-cell and B cell in malignancy where little effect is exerted on normal cell.
- Effect on inflammatory response
- Glucocorticoids are powerful anti-inflammatory agents. GCs causes the inhibition of Chemotaxis (recruitment of the cell at the site of inflammation).
- Effect on immunity
- These hormone suppresses cell-mediated immunity (CMI)more than humoral immunity & act as immunosuppressant. Immunosuppressive effect of glucocorticoids is used to prevent graft rejection and various hypersensitivity reaction.
Corticosteroids Drugs: Pharmacology

Note:- Most potent MCs – Aldosterone
Hydrocortisone has both MCs & GCs Activity. (Equal MCs :GCs :: 1 : 1 activity)
Betamethasone & Dexamethasone has Zero MCs activity so that it is used in Cerebral edema inflammation.
Most Potent GCs – Dexamethasone
Most potent MCs: Fludrocortisone
DOCA = GCs activity = Zero
Use of corticosteroids (Glucocorticoids & Mineralocorticoids)
1. Hormone Replacement Therapy/HRT
- Acute Adrenal Insufficiency: i.v. hydrocortisone
- Chronic adrenal insufficiency (Additions disease: Hydrocortisone & MCs- Fludrocortisone
- : Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) /Adreno genital syndrome
- Lack Enzyme 21- hydroxylase-Synthesis of corticosteroids suffers/decrease- ACTH compensatory- Enlargement of Adrenal gland for more corticosteroid synthesis.
- This is result of congenital deficiency of the enzyme involved in the synthesis of corticosteroids. Due to decreased corticosteroid/ adrenal secretion, there is no feedback inhibition of the pituitary and consequently ACTH secretion increases. This results in overgrowth of the adrenal gland. So in the treatment of CAH is aimed to reduce ACTH secretion. EXOGENOUS glucocorticoids like hydrocortisone cause feedback inhibition of HPA Axis.
- Diagnostic use: Dexamethasone suppression Test is used to test the intactness of HPA axis function and diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome.
2. Non Endocrine use / pharmacotherapy
- RAs-Rheumatoid arthritis (Adjv) & Gout (Acute) short as Anti-inflammatory
- Anti inflammatory – Allergy like Anaphylasis (but DOC is Adrenaline) & Asthma
- Immunosuppresant : Autoimmune disease & to prevent organ transplant rejection
- Rheumate fever
- SLE
- Lung maturation /surfactant production in the foetal: Dexamathasone is given to accelerate the fetal lung maturation.
- Cheomotherapy malignancy
- Opthalmic as Anti-inflammatory like conjunctivitis, iritis, iridocylitis & keratitis.
- Skin as anti Allergy (), but steroids are contraindicated in herpes simples keratitis.
- Cron disease
- Thyroid storm
- Septic shock
- GIT – ulceration colitis
Cushing Disease Syndrome:-
It is characterized by excessive secretion of Corticoids.
Treatment:-
- Mefepristone
- Trilostone
- Ketoconazole
- Aminoglutethimide
The important point for Systemic use of Steroids
The steroid should not be withdrawal abruptly because it may precipitate acute adrenal insufficiency.
A large single dose is less harmful than a small dose given for long periods. 80 mg prednisolone for 2 days is much less harmful than 20 MG dose for 6 months.
Glucocorticoid synthesis inhibitors
Glucocorticoid synthesis inhibitors are useful in the treatment of Cushing syndrome and diagnosis of adrenal disease.
- Metyrapone
- Aminoglutethimide
- Mitotane
- Trilotane
- Ketoconazole
Corticosteroid receptor antagonist
- Mifepristone
- Spironolactone & Epleronone
- Drospirenone
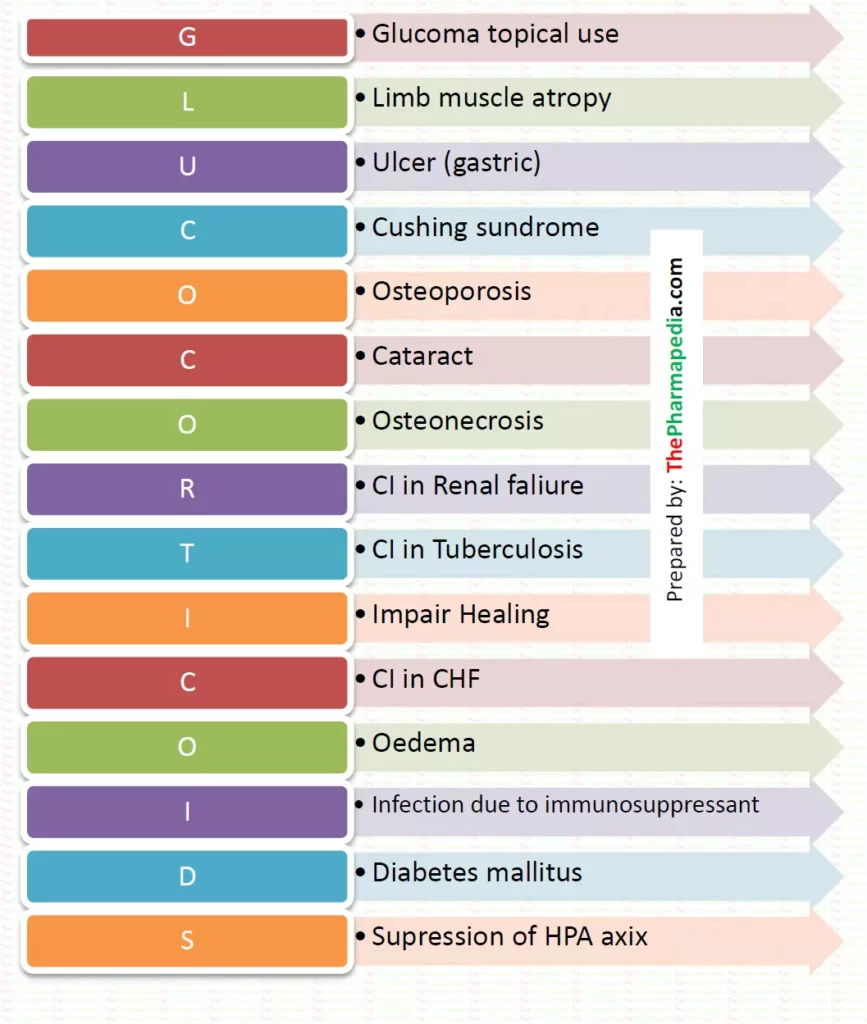
Adverse effect & Contraindication of Steroids


Comments are closed