A. Disease:
Any harmful deviation from the normal functional/ structural state of an organism/ person. The normal state of the organism (human/plant) represents the condition of physiological balance (homeostasis).
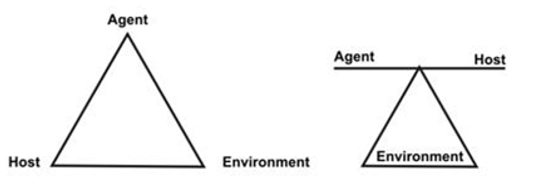
B. Epidemiologic triad
The traditional model for infectious disease:- Interaction of these three factors is necessary to initiate the disease process (agent, host & environment). These three factors are referred to as an epidemiological triad.
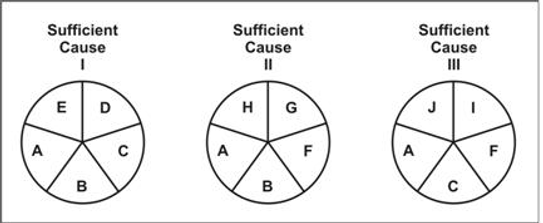
C. Rothman’s Causal Pies:
The agent-host-environment model did not work well for many non-infectious diseases, Causal Pies was proposed by Rothman.
D. Natural history of disease:
A study of the evolution of the disease from the earliest stage (pre pathogenesis) to its termination (recovery, disability or death).
Natural history of the disease is used for the prevention of disease
Natural history of the disease is established by:
i. Cohort studies
ii. Cross-sectional studies
iii. Retrospective studies
Phase of the natural history of disease- 2 phases
i. Prepathogenesis
(process in environment, agent has not yet entered in host/person)
ii. Pathogenesis
((in person, begin with the entry of agent, incubation, early and late petrogenesis into host/person)
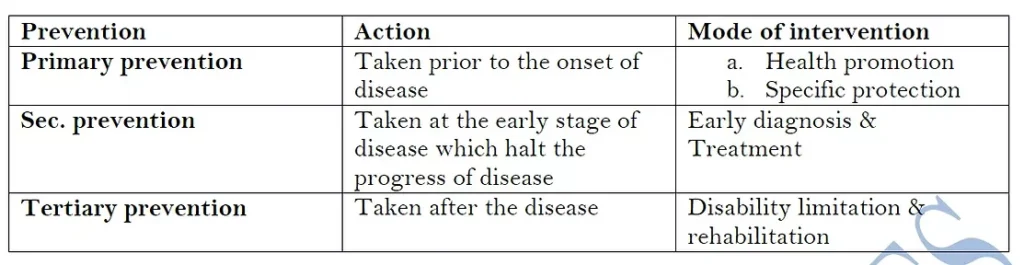
E. Prevention of disease (3 levels)
F. Emerging infectious diseases:
These are infections that have recently appeared within a population or those whose incidence or geographic range is rapidly increasing or threatens to increase in the near future or existing disease that has recently developed new clinical pattern, or developed resistance to existing therapy. Emerging infections can be caused by:
- Previously undetected or unknown infectious agents
- Known agents that have spread to new geographic locations or new populations
- Previously known agents whose role in specific diseases has previously gone un-recognized.
- Examples:
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) & MERS
- H1N1 (bird flu/avian influenza): positive in India was reported on May 2009, from a passenger who traveled from the USA arriving at Hyderabad airport.
- H5N1
- chikungunya virus, Dengue, Zika virus, Nipah & Ebola virus, Meningococcal disease
- Re-emerging infectious diseases(EIDs):
- Re-emergence of agents whose incidence of disease had significantly declined in the past, but whose incidence of the disease has reappeared. This class of diseases is known as re-emerging infectious diseases.
- Example: Chikungunya (2003 than re-emerge in 2007 after 3 years)
- Re-emergence of agents whose incidence of disease had significantly declined in the past, but whose incidence of the disease has reappeared. This class of diseases is known as re-emerging infectious diseases.
- RNTCP: Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (1997)
- DOTS: directly observed treatment short course
- NTP: national tuberculosis program (1962)
- NSP: national strategic program for tuberculosis elimination (2017-2025) to control tuberculosis by 2025; for strategic pillar-DTPB( detect, treat, prevent & build)
- NIKSHAY: web based tuberculosis surveillance system
- NIKSHAY POSHAK YOJNA: 500 INR- incentive via DBT
- NLCP: National leprosy Control Programme (1955)
- NLEP: National leprosy eradication programme (1983)
- NVBDCP: National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme
- IDSP: integrated disease surveillance project
- NTCP: National tobacco Control Programme
- NIDDCP: National iodine deficiency disorder Control Programme (Iodine: essential micronutrients, Delhi requirement 100-150 microgram; salt 15 PPM)
- NACP: national AIDS control programme
- NVHCP: National Viral hepatitis control program (28th JULY 2018 ON WORLD HEPATITIS DAY)
Join Our WhatsApp Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to Download Free Books & Notes, Previous papers for D.Pharm, B.Pharm, M.Pharm, Drug Inspector & GPAT……….

Comments are closed