The tablets formation process consists of a series of steps (unit processes)– weighing, milling, mixing, granulation, drying, compaction, coating and packaging.
UNIT DOSE OPERATIONS: Every separate manufacturing step is called a “Unit Operation”. Weighing, Blending and Tabletting are individual unit operations. A “Batch” of powder or granulation is processed in each unit operation.
Manufacturing of Tablets (pharmaceutical)
Steps involved in the proccesing of tablets:
- Preparation of granules for compressing
- Weighing the ingredients
- Pulverization & Mixing
- In this step solid powder ingredient are reduced to the same size
- Done to protect from segregation during mixing
- Convention of mixed
- Compression of granules into tablets
- Coating of tablets
- Evaluation of tablets
Tablets made by blending the dry powdered ingredients together, and then compressing into tablets is called “A Directly Compressible Formula”.
If powders will not make a good tablet because they do not compress, don’t flow well, are too fluffy or separate after blending, the particles need to be combined and attached using a pharmaceutical glue called a binder. When the binder is put into water or a solvent solution and is sprayed or metered into the powders this process is called “The Wet Granulation Process”. The solids within the liquid solution form bonds between particles which are maintained even after the liquid is dried and milled. There are many different types of binders that can be used.
Many powders require some level of intense mixing while adding a liquid binder, actually comparable to kneading dough when making bread. Once the powder and binding solution are kneaded they are then milled for drying. The bonds that hold the particles together can withstand the milling process forming a uniform size “granule”. If we accomplish these “unit operation” steps correctly (pre-blending, binder addition, milling, drying and final blending) the result is a compressible powder called a granulation.
Granulation is the formation of small agglomerates called“granules”. Each granule will contain a proper mix of the ingredients of the formula. We can control the final density of the granules by the amount of liquid binding solution and the mechanical energy created by the type of machine used. The machines used to blend powders and add liquid are called “granulators”.
Wet granulation must be moved to the next unit operation which is called Drying.
When powders are sensitive to liquids, heat, or both, we must blend the powders with a pre granulated “dry binder”. If the blended powders will not work with the addition of the dry binder and liquid, or heat cannot be used, then we must “Dry Granulate”. The Dry Granulation method uses mechanical force to densify and compact powders together which forms dry granules. This compaction can be done on a tablet press using “slugging tooling”. Slugging tooling or slugging punches & dies are a method to dry compact powders into granules.
The other method is to use a machine called a Roller Compactor or Chilsonator. This is basically the same kind of machine used to make the charcoal briquettes for our outside grill. The slugged or roller compacted powders are then milled, final blended and compressed on a tablet press.
Of these three principle methods, the “Wet Granulation” method is the most common.
Tablets are manufactured by
- Direct compression
- Wet granulation
- Dry granulation
Manufacturing of Tablets (pharmaceutical)
Steps involved in the proccesing of tablets:
- Preparation of granules for compressing
- Weighing the ingredients
- Pulverization & Mixing
- In this step solid powder ingredient are reduced to the same size
- Done to protect from segregation during mixing
- Convention of mixed
- Compression of granules into tablets
- Coating of tablets
- Evaluation of tablets
Tablets made by blending the dry powdered ingredients together, and then compressing into tablets is called “A Directly Compressible Formula”.
If powders will not make a good tablet because they do not compress, don’t flow well, are too fluffy or separate after blending, the particles need to be combined and attached using a pharmaceutical glue called a binder. When the binder is put into water or a solvent solution and is sprayed or metered into the powders this process is called “The Wet Granulation Process”. The solids within the liquid solution form bonds between particles which are maintained even after the liquid is dried and milled. There are many different types of binders that can be used.
Many powders require some level of intense mixing while adding a liquid binder, actually comparable to kneading dough when making bread. Once the powder and binding solution are kneaded they are then milled for drying. The bonds that hold the particles together can withstand the milling process forming a uniform size “granule”. If we accomplish these “unit operation” steps correctly (pre-blending, binder addition, milling, drying and final blending) the result is a compressible powder called a granulation.
Granulation is the formation of small agglomerates called“granules”. Each granule will contain a proper mix of the ingredients of the formula. We can control the final density of the granules by the amount of liquid binding solution and the mechanical energy created by the type of machine used. The machines used to blend powders and add liquid are called “granulators”.
Wet granulation must be moved to the next unit operation which is called Drying.
When powders are sensitive to liquids, heat, or both, we must blend the powders with a pre granulated “dry binder”. If the blended powders will not work with the addition of the dry binder and liquid, or heat cannot be used, then we must “Dry Granulate”. The Dry Granulation method uses mechanical force to densify and compact powders together which forms dry granules. This compaction can be done on a tablet press using “slugging tooling”. Slugging tooling or slugging punches & dies are a method to dry compact powders into granules.
The other method is to use a machine called a Roller Compactor or Chilsonator. This is basically the same kind of machine used to make the charcoal briquettes for our outside grill. The slugged or roller compacted powders are then milled, final blended and compressed on a tablet press.
Of these three principle methods, the “Wet Granulation” method is the most common.
Tablets are manufactured by
- Direct compression
- Wet granulation
- Dry granulation
1. Direct compression
The tablets are made by directly compressing the powdered materials without modifying the physical nature of the materials itself.
Direct compression is generally done for the crystalline materials having good physical properties such as flow property, compressibility etc.
The main advantages of direct compression are time-saving, the safety of operations and low cost.
E.g. NaCl, KCl can be directly compressed
Uses directly compressible diluents like spray-dried lactose
Steps: Weighing – Mixing – Screening – Compression
2. WET GRANULATION
Wet granulation is the most commonly used method for the production of compressed tablets.
Granulation is the formation of small agglomerates called “granules”. Each granule will contain a proper mix of the ingredients of the formula. The machines used to blend powders and add liquid are called “granulators”.
Many granulators do not have the ability to dry the wet massed granulation; therefore the wet granulation must be moved to the next unit operation which is called Drying.

In this method, the powders are bound by a suitable binder by “adhesion”. The binder is added by diluting with a suitable solvent prior to addition to the blended powders to form wet granules which in turn are dried suitably to expel the solvent forming dried granules.
The surface tension forces and capillary pressure are primarily responsible for initial granules formation. The main advantage being it meets all the requirements for tablet formation though it is multistage, time-consuming.
Advantage of Granulation
- To improve powder flow.
- To improve compressibility.
- To reduce fines.
- To control the tendency of powders to segregate.
- To control density. To capture and fuse small quantities of active material.
How Granules are tested
There are four standardized tests that are commonly performed on either milled or finished granules-
- LOD (Loss on Drying)- water content
- Bulk Density, mg/ml
- Particle Size Distribution
- Angle of Repose, flow gradient.
3. Dry granulation
The dry granulation process is used to form granules without using a liquid solution. This type of process is recommended for products, which are sensitive to moisture and heat. Forming granules without moisture requires compacting and densifying the powders.
Dry granulation can be done on a tablet press using slugging tooling. On a large-scale roller compactor commonly referred to as a chilsonator. The compacted mass is called slugs and the process is known as slugging.
The slugs are then screened or milled to produce a granular form of tablet materials, which have the good flow properties then original powder mixture.
The main advantage of dry granulation is it requires less equipment and eliminates the addition of moisture and the application of heat, as found in wet massing and drying steps of the wet granulation method.
The Dry Granulating method is used over other technologies for one or more of the following reasons:
- 1. Granulate materials which are sensitive to heat and/or moisture.
- 2. Produce a uniform particle size range.
- 3. Improve flow properties.
- 4. Control dust.
- 5. Control bulk density.
- 6. Produce uniform blends
- 7. Control particle hardness.
- 8. Improve wetting or dispersion rates.
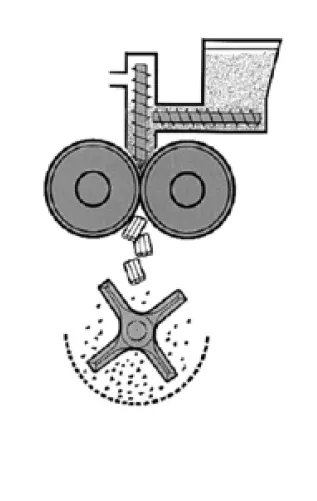
The manufacture of oral solid dosage forms such as tablets is a complex multi-stage process under which the starting materials change their physical characteristics a number of times before the final dosage form is produced.
Traditionally, tablets have been made by granulation, a process that imparts two primary requisites to formulate: compactibility and fluidity.
Regardless of whether tablets are made by direct compression or granulation, the first step, milling and mixing, is the same; subsequent steps differ.
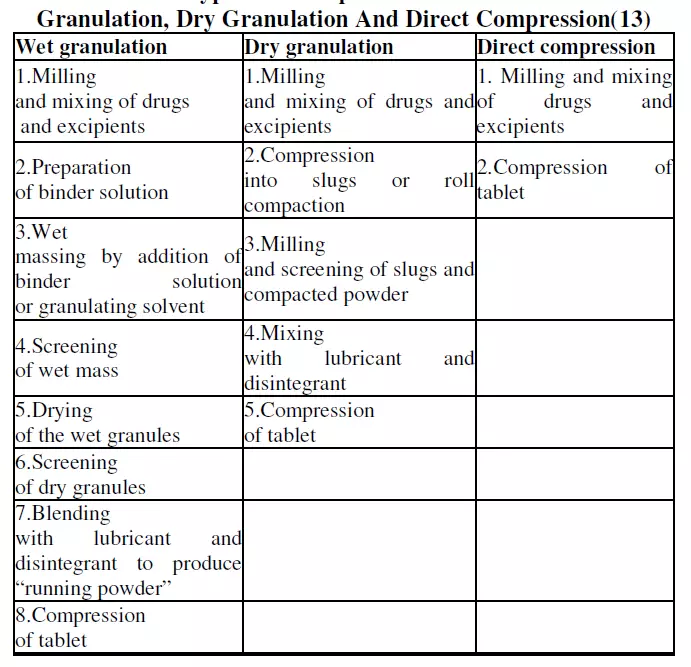
Summery of Wet Granulation, Dry Granulation & Direct Compression
Join Our WhatsApp Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to Download Free Books & Notes, Previous papers for D.Pharm, B.Pharm, M.Pharm, Drug Inspector & GPAT……….

