Freeze dryer/ lyophilization
Freeze drying or lyophilization is a drying process used to convert solutions into solids powder of sufficient stability for distribution and storage. Freeze drying is also known as Lyophilization, gelsiccation or drying by sublimation.
Many pharmaceutical products lose their potency/viability in liquid state if dried in air at normal atmospheric pressure. while some products may heat sensitive or oxygen sensitive. So to stabilize such type products, freeze drying is used for drying.
Example: Blood serum, plasma, antibiotics, hormones, bacterial cultures, vaccines etc
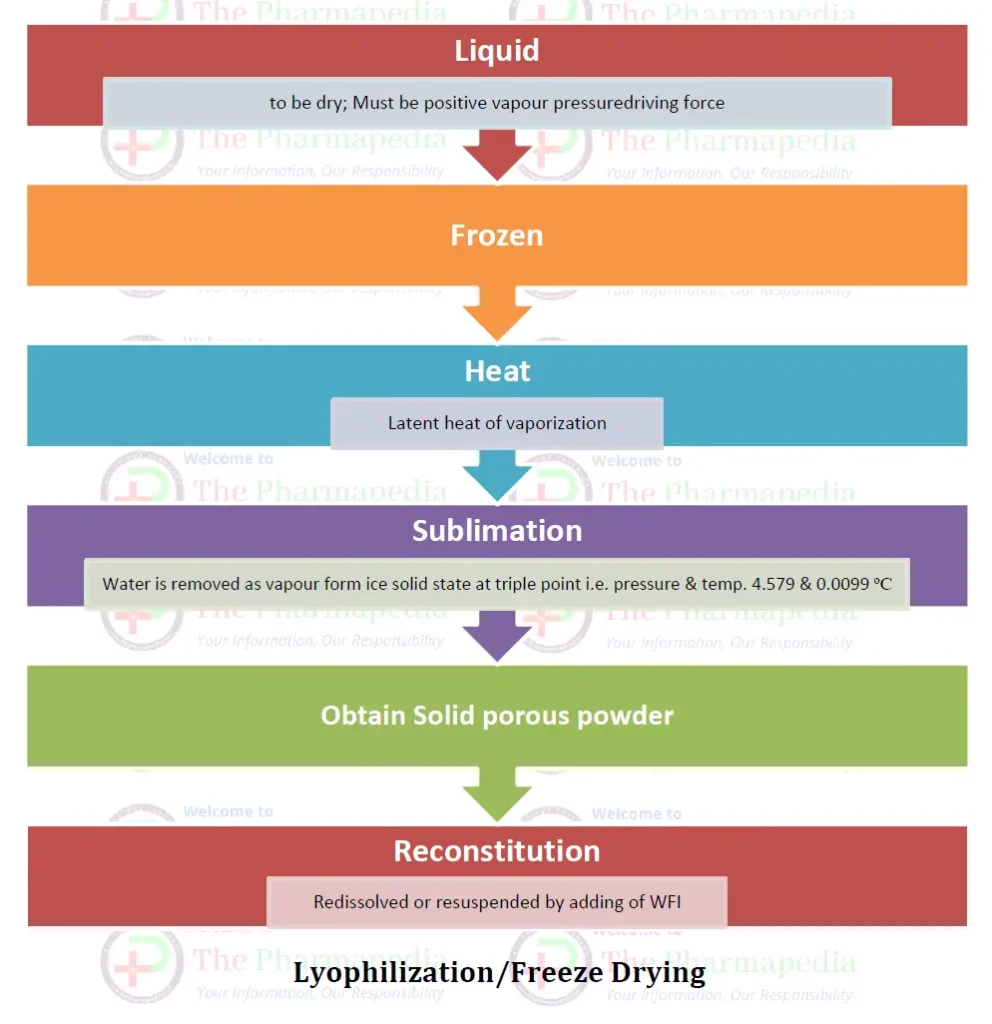
Principle of Freeze Dryer: Sublimation
The main principle involved in lyophilization is a phenomenon called sublimation, where water is removed directly from solid state (ice) to the vapour state without melting.
Sublimation take place at/below triple point of pressure & temperature i.e. 4.579 mm Hg & 0.0099 oC
The water passes directly from the solid state (ice) to the vapor state without passing through the liquid state. Water is removed from the frozen state material and then subjected to high vacuum to heat (by conduction or radiation or by both) so that the sublime frozen liquid leaving only solids or the dry components of the original liquid. Drying is achieved by subjecting the material to temperature and pressures below the triple point.
Basic Requirement of Freeze drying
In respect of liquid to be dried
- The vapour pressure of the water on the surface of the material being dried must be higher than the partial pressure of the enveloping atmosphere, i.e. there must be a positive vapour pressure driving force.
- The latent heat of vaporization must be introduced to the drying solid.
- Provision must be made for the removal of evaporated moisture.
Construction & components of Freeze Dryer:
The construction of freeze dryer is made of four basic components
- A Drying Chamber– Drying chamber in which trays are loaded for vacuum drying.
- Heat source- Heat supply in radiation source, heating coils to provide latent heat of vaporization.
- Vacuum Source- To remove air/oxygen vacuum pump or stream ejector or both are used.
- Vapour removal system- condensers, desiccants, pumps or adsorption system.
- The freeze dryer consist of drying chamber in which shelves are used to place the material.
- Heat supply is in the form of radiation source by using heating coils.
- The condenser is also attached. Condenser consist of large surface cooled by solid carbon dioxide slurred with acetone or ethanol. The condenser surface should be cleaned properly. The purpose of the condenser is to attract the vapors being sublimed off of the product. Because the condenser is maintained at a lower energy level relative to the product ice, the vapors condense and turn back into solid form (ice) in the condenser. In shelf freeze dryers, the condenser can be located inside the product chamber internal condenser) or in a separate chamber (external condenser) connected to the product chamber by a vapor port. The distance between subliming surface and condenser should be less than mean path of molecules. Because this increases the rate of drying.
- The vacuum pump is also connected which cause evaporative cooling. The vacuum system consists of a separate vacuum pump connected to an airtight condenser and attached product chamber.
Working of Freeze Dryer:
The following steps are involved in the working of freeze dryer
Working The working of freeze dryer consist of following steps.
1. Preparation & pre-treatment
Pretreatment includes any method of treating the product prior to freezing. This may include concentrating the product, formulation revision (i.e., addition of components to increase stability, preserve appearance, and/or improve processing), decreasing a high-vapor-pressure solvent, or increasing the surface area. This reduces the actual drying by 8 to 10 times.
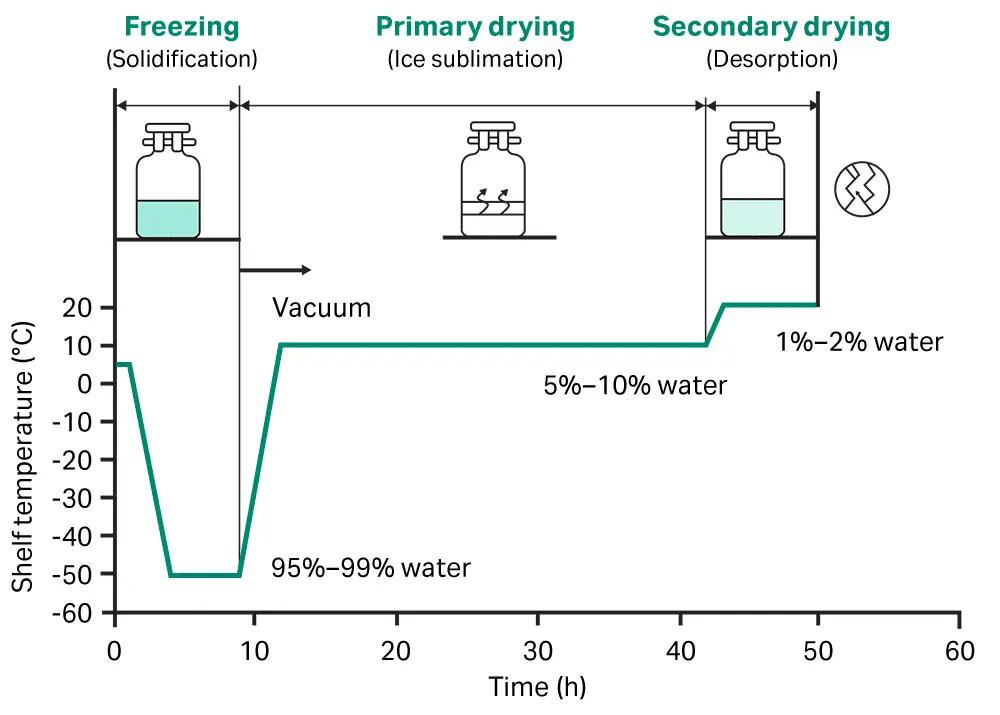
2. Pre-freezing to solidify water
Vials, ampoules or bottles in which the aqueous solution is packed are frozen in cold shelves (below −20°C). Pre-freezing of the material is done before application of vacuum avoids foaming.
The normal cooling rate is about 1 to 3 Kelvin/ minute so that large ice crystals with relatively large holes are formed on sublimation of ice. This is also responsible for giving a porous product.
3.Vacuum
Rotary pumps on small scale, and ejector pumps on large-scale, are used to reduce the pressure sufficiently.
4. Primary Drying (sublimation of ice under vacuum)
During primary drying the latent heat of sublimation must be provided and the vapour removed.
Primary drying stage by sublimation can remove the unbound water.
Primary drying stage removes easily removable water, about 98% to 99%.
The temp. & pressure should be below the triple point of water i.e. 0.0098ᵒC & 4.58 mmHg for sublimation, when water is alone present.
When a Solution of a solid is dried, the depression of freezing point of water occurs. Hence, it is essential that the temperature be brought below the eutectic point. The pressure & temp. at which the frozen solid vaporizes without conversion to liquid is referred to as the eutectic point.
4. Secondary Drying
It is removable of residual moisture under high Vacuum. The temp. of solid is raised to as high as 50 to 60ᵒC but vacuum is lowered below that is used in primary drying. The rate of drying is very low & it takes about 10 to 20 hrs.
5. Packing
After vacuum is replaced by inert gas, the bottles & vials are closed.
Animation of Freeze drying (courtesy-youtube)
Application of Freeze Drying
Lyophilization is suitable for drying of materials that are
- Oxygen sensitive materials (so applied vacuum)
- Drug that are unstable in liquid state (final product is powder solid)
- Heat sensitive materials (apply freezing technique)
Advantage
- heat-sensitive drugs and biologicals can be dried at low temperatures without damaging
- Freeze-dried products can be reconstituted quickly and easily since final product is porous.
- Can be dried oxygen sensitive material or materials that are oxidized in air( Since lyophilization is carried out under vacuum)
- Reduced weight and volume make lyophilized samples ideal for shipping.
- Less chance of contamination under aseptic condition
Disadvantage
- Water for injection (WFI) required for reconstitution of the freeze dried product
- Slow process
- Airtight containers are required for long-term storage
- Need of high vacuum
- High unit cost
Also Read…
Fluidized Bed Dryer (Principle and Working)
Join Our WhatsApp Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to Download Free Books & Notes, Previous papers for D.Pharm, B.Pharm, M.Pharm, Drug Inspector & GPAT……….
