Aerosol packages consist of various components including

1. Propellant
Propellants used for pharmaceutical aerosol are accountable for generating proper expelling pressure within the container to expel its contents
- Liquefied gases propellants
- Hydrocarbons
- Compressed gases propellants

a) Liquefied gases
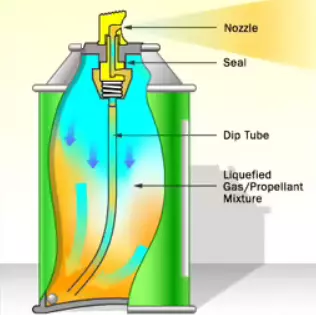
The liquefied gases stay in the form of gases phase at normal atmospheric pressure and temperature. By elevating the pressure or lowering the temperature below their boiling point, Liquefied gases are liquefied.
Once these liquefied gases are packed into sealed containers, they change into liquid and vapor phases. The pressure inside the pressurized aerosol container gradually increases throughout the formation of the vapor phase until establishing equilibrium between the liquefied propellant phase and vapor phase. The liquid contents of the aerosol are pushed against the valve by the action of this pressure, and upon releasing of the valve, the liquid will expel and come in contact with room temperature and atmospheric pressure, thus causing the liquefied propellant to reappearance back to the vapor state, leaving the other components to deposit on the surface they are supposed to function upon.
- Liquefied propellant are gases that exist as liquid under pressure
- Most widely used propellant in pharmaceutical preparation.
- These are inert, non-toxic and non-inflammable.
- These are gases at room temperature and atmospheric pressure.
- Can be liquefied easily by lowering the temperature or by increasing the pressure.
- Dispensing active ingredients into fine Mist or foam.
- These gases maintain a constant pressure within the container.
- Example:
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC)
- Hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFC)
- Hydrofluorocarbons (HFC)
Chlorofluorocarbons
- Fluorinated hydrocarbons are widely used in aerosol for oral and inhalation use.
- Chemical inertness
- Lake of toxicity
- Non-inflammatory e
- Lack of explosiveness
- Example
- Trichloro mono fluoro methane-propellant 11
- Dichlorodifluoromethane- propellant 12
- Dichlorotetrafluoroethane- propellant 114
- HCFC & HFC
- Heptafluoro propane (HFA-229)
- Tetrafluoroethane (HFA-139a)
- Difluoroethane -Propellant 152A
b) Hydrocarbon
- These are flammable but less toxic, less dense, more economic, more soluble and chemically more stable.
- Used for topical pharmaceutical aerosol
- Example:
- Propane -propellant A108
- Butane -Propellanr A-17
- Isobutane- propellant A 31
c) Compressed gases
- Compressed gases has little expansion power
- Compressed gases produce a fairly wet spray and less stable foam as compared to liquefied gases propellant
- Example: Nitrogen, Nitrous oxide and Carbon dioxide
- Compressed gases are used in topical pharmaceutical aerosols
- No chilling effect at the site of application on the skin
- Compressed gases used as a propellant in topical pharmaceutical aerosol like hair preparations, ointment, dental creams, Aqueous germicidal and antiseptic aerosol, contact lenses cleaners etc
- Compressed gases are limited value in aqueous products since propellant and water are not miscible
2. Container
There are containers in which the product concentrate is filled.
Container for aerosol must withstand pressure as high as 140 to 180 psig (pound per sq. inch gauge) at 130 degrees Fahrenheit including metal and glass containers.
The metal container includes tin-plated Steel, aluminium and stainless steel whereas the glass container includes uncoated glass and plastic coated glass.
a) Metal
- Tin-plated steel
- Side-seam/three piece
- Two-piece or drawn
- Tin-free steel
- Aluminum
- Two-piece
- one-piece (seamless/extruded or drawn)
- Stainless steel
b) Glass
- Uncoated glass
- Plastic coated glass

Tin plated steel containers
Consists of a sheet of steel plate that has been electroplated on both side with tin.
Tin-plated metal containers are suitable for non-aqueous product alcohol base Pharmaceuticals
If Aqueous product with a low pH, the tin-plated container must be subject to the organic lining of epoxy and or Vinyl resin to avoid incompatibility or any corrosion.
Aluminum containers
Aluminum containers are seamless, resistant to corrosion and exhibit lesser incompatibility problem.
Precautions: anhydrous ethanol is extremely corossive to aluminium. This can be prevented by anodizing the aluminum and adding water(2 to 3%) to the formula.
Stainless steel containers
Stainless steel containers are extremely strong and resistance to most materials but they are costly
These containers are used for inhalation aerosol packaging.
Glass containers
Maybe uncoated or plastic coated.
Glass containers are flexible in design
Absence of corrosion problems in glass containers.
Highly compatible with Pharmaceutical preparation.
Limitation of the Glass container
Brittleness and breakage problem with glass containers.
Not bear a high pressure, so pressure should be below 25 psig.
The plastic coating is done to increase withstand more pressure up to 33 psig.
3. Valve & Actuator
The aerosol valve is a very important part of an aerosol container; it is a vital part responsible for expelling and dispensing the desired dose of the aerosol contents in the desired controlled rate. Valves account for delivering the product concentrate in the preferred form and controlling the flow rate of contents from the container.
An aerosol valve is a unique feature of this dosage which is a vital part for effective expelling and dispensing the desired dose of the aerosol contents in the controlled rate. Various types of aerosol valves are used depending on the physical form dispensed and how the aerosol to be used.
The types of the valves are variable; mainly two types are applicable—either a continuous spray valve or a metering valve.
Continuous spray valves
To deliver the product contents constantly in the form of a spray or solid foam stream with or without amount determination. These kinds of valves are the main type used for all categories of pharmaceutical aerosols.

Metering valves
To deliver the contents for potent medication, they are dispensing the exact amount of medicament upon each time of activation during application.

Pharmaceutical aerosol maybe dispense with required doses as in the form of
- Spray
- Foam
- Solid stream
The aerosol valve assembly consists of many different parts as follow shown in figure
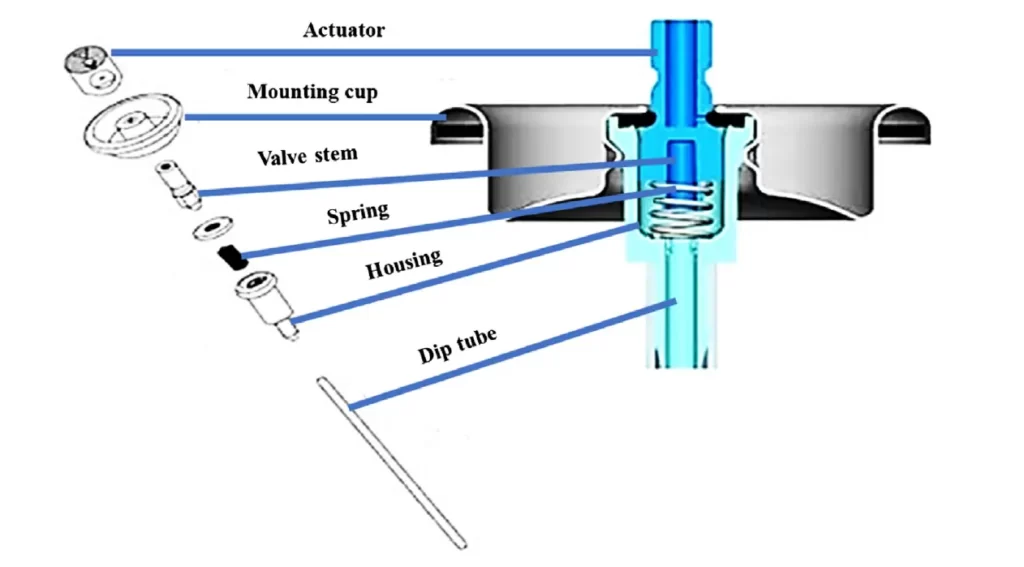
The basic parts of a valve assembly
Actuator:

It is a Specially designed Button fitted to the valve stem which ensure proper delivery the aerosol product in the desired form (spray, foam or solid stream).
or
It is the push knob which the user presses to activate or deactivate the assembly of the valve system. The physical form of the emitted product concentrate is determined by the combination of the type and amount of propellant used along with the proper actuator design and dimensions.
TYPES OF ACTUATORS :
• Spray actuators
• Foam actuators- Large orifice relatively
• Solid steam actuators
• Special actuators
2. Stem:
Provides necessary support for the actuator and delivers the contents in the desired form to the chamber of the actuator.
Stem is made of Nylon or Delrin.
Gasket:
It is made from Buba-N & Neoprene rubber & compatible with most pharmaceuticals. it erves to prevent leakage of the product concentrate when the valve is in the deactivated position, placed tightly with the stem.
Spring:
Stainless steel spring is used to hold the gasket in place & when actuator is depressed & releases, it returns the valve to its closed position.
Ferrule or Mounting Cup:
It is attached the valve proper to the containers & are ususally attached the container either by rolling the end under the tip of bottle or by clinching the metal under the lip.
Valve body or Housing:
It comprises of an opening at the point of the attachment of the dip tube, ranging from 0.013 inch to 0.080 inch & made of Nylon/Delrin. The housing may or may not continaer another opening referred to as the Vapor tap.
Vapor tap allows for the escape of vaporised propellant alog with the liquid product & is available in sizes ranging from 0.013 to 0.080 inches.
It further produces a fine particle size, prevents valve clogging with product containing insoluble materials, allows for the product to be satisfactory dispensed with the container in the inverted position, reduces the chilling effect of the propellant on the skin & in the case of hydrocarbons propellant, allows for decrease in flame extension.
Dip tube:
It is the part of the valve assembly that extends downstream into the product concentrate aids to transport the contents from the container to the valve.
Dip tubes are made from Polyethylene or polypropylene. Polypropylene tube is usually more rigid/hard.
Inner Diameter of dip tube is selected based on desired viscosity & delivery rate (0.050-0.195 inch)
Metering valve
These are used for the dispensing of Potent medication with an accuracy of dosage.
50 to 150 mg (10% variation) of liquid material can be dispensed with metering valves.
| Components | Material of construction |
| Ferrule or mount cap | Aluminum or Brass |
| Valve body or housing | Nylon, Delrin |
| Stem | Nylon, Delrin or Aluminium |
| Gasket | Buna-N and Neoprene |
| Spring | Stainless steel |
| Dip tube | Polypropylene and polyethylene |
4. Product concentrate
Product concentrate of an aerosol in which the active drug combined with suitable excipients can be delivered in three forms of liquid form a solution, suspension, an emulsion or in a form similar to semisolid.
Also, Read……..
Aerosols Evaluation Parameters
Universal tests & Standard for Pharmaceutical Aerosols
Join Our WhatsApp Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to Download Free Books & Notes, Previous papers for D.Pharm, B.Pharm, M.Pharm, Drug Inspector & GPAT……….

Comments are closed