- Histamine – Derived from-histidine -stored in mast cell with Heparin.
- Type of Histamine Receptor – 4 types
- H1
- H2
- H3
- H4– Allergic & inflammation
- Histamine Non-selective agonist at H1+ H2+ H3 Receptor
- Selective H1-Agonist-2-methyl histamine, 2-pyridyl-ethyl amine, 2-Thiazolyl ethylamine
- Selective H2 –Receptor agonist – 4-methyl histamine, Dimaprit, Impramidine
Action/Role of Histamine:
- Blood Vessel :- Dilation of Small Blood vessel Flushing & hypotension
- Increase capillary permeability Edema through H1 Receptor
- Intradermal Inj. :- Triple Response due to Primarily H1 – Receptor mediated
- Red Rxn. = due to Vasodilation
- Wheal = Exudation of fluid due to increased permeability
- Flare = Spreading redness due to Axon reflex
- Visceral smooth muscle:- Powerful contractor of visceral S.M via H2 Receptor Bronchoconstriction & abdominal cramps via H1 receptor
- Gastric :- Increase Acid secretion gastric secretion by stimulation of H2-Histaminic Rec.
- Neuron – Stimulates nerve ending – may result in pruritis & pain
- Brain – Maintain wakefulness through H1-Receptor – Block LCZ
- Histamine (H1) – serve as a mediator of inflammation & immediate type of hypersensitivity reaction.
Note:-
Betahistine:- Histamine analogue – used to control vertigo in Meniere’s disease
H1 Anti – Histaminic:- These drugs act as competitive antagonist at H1-Receptor.
Classification of Anti-histaminic Drugs
On the basis of CNS penetration & Anticholinergic properties, Anti-histaminic drug are classified into 1st generation & 2nd generation.
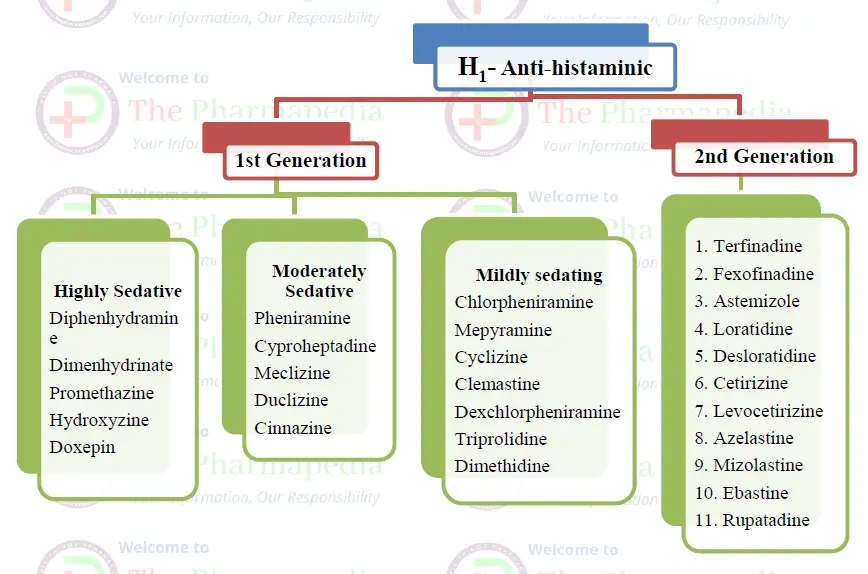
1st Generation – Anti-histaminic (H1):-
- Can penetrate BBB Sedation & psychomotor impairment so 1st generation Anti-histaminic contradicted in person requiring constant attention (like driving, machinery operators, swimmers etc)
- 1st Anti-histaminic also posses Anti-Cholinergic activity
- Major Adverse effect of 1st Generation = Sedation, Psychomotor impairment & Anti-cholinergic effects (dryness of mouth, blurred vision, urinary retention, constipation etc)
2nd Generation Anti-histaminic (H1)
- Little CNS penetration (No sedation)
- No Anti-Cholinergic activity
- Additionally has Anti-allergic [Cetrizine & Axelastine]
Use of Antihistaminic drugs
| Based on H1-Blocking action | Based on Anti-cholinergic properties | Other uses |
| Allergic condition – itching, urticaria, hay fever etc.Insect bite, prevention of adverse effect due to histamine release | Common cold to control rhinorrhoeaMotion sickness (Prophylactic)Parkinsonism (promethazine)Acute muscular dystonia | Idiopathic pruritis Anti-vertigo (cinnarizine) |
Note:
- Cetrizine – It is active metabolite of 1st generation drug hydroxyzine.
- Levocetirizine – ‘l’ isomer of cetrizine
- All second generation Anti-histaminic are metabolized to active product except cetrizine & mizolastine.

Comments are closed