Quality Control (QC) tests For Parenteral Product
QA (Quality Assurance) relates to the studies made and the plans developed for ensuring the quality of a product.
QC (Quality Control) includes the carrying out of these QAs plans during production and includes all of the tests and evaluations performed to ensure quality exists in each specific lot/batch of products.
Evaluation of Parenteral Preparations
- Sterility test
- Membrane filter method
- Direct inoculation method
- Pyrogen test
- LAL Test
- In vivo Rabbit test
- Clarity test/Foreign particulate matter test
- Leakage test
- Isotonicity
- Content uniformity & Weight
- Extractable Volume

1. Sterility test
Sterility test is applied to pharmaceutical preparations that are required to be sterile like parenteral & ophthalmic preparation.
A sterility test is carried out to detect the presence of a viable form of microorganism in the all-injectable preparation of each lot.
A sterility test must be carried out under aseptic conditions (a grade ‘A’ laminar airflow cabinet or an isolator is recommended)
Sterility-Incubate portions of the media for 14 days at the temperatures indicated under each medium. No growth of micro-organisms occurs.
There are two general methods for sterility testing:
1) Membrane Filtration: Method ‘A’
2) Direct inoculation method: Method ‘B’
Either of the following methods, Method A – Membrane Filtration or Method B – Direct Inoculation, may be used for sterility test.
a. Membrane Filtration method
- 0.2 m membrane (not more than 0.45 m) & Diameter;- 50 mm
- Used for
- An oil
- An ointment that can be put into the solution
- A non bacteriostatic solid not readily soluble in the culture medium.
- A soluble powder or a liquid that possess inherent bacteriostatic or fungistatic properties.
- For liquid products where the volume in a container is 100m1 or more.
- This method basically involves filtration of Sample through membrane filters
b. Direct Inoculation method
- Aseptically opening each sample container from a recently sterilized batch of product.
- Using a sterile syringe and needle to withdraw the required volume of sample for both media from the container
- Injecting one-half of the required volume sample into a test tube containing the required volume of FTM and the other half volume of sample into a second test tube containing the required volume of SCD and incubating both.
Culture Media for Sterility Test
The following culture media have been used for the sterility test of sterile pharmaceutical products.
The fluid thioglycollate medium is primarily intended for the culture of anaerobic bacteria; however, it will also detect aerobic bacteria. Soya-bean casein digest medium is suitable for the culture of both fungi and aerobic bacteria.
1. Fluid thioglycollate medium
2. Alternative Thioglycollate Medium
3. Soyabean-casein Digest Medium
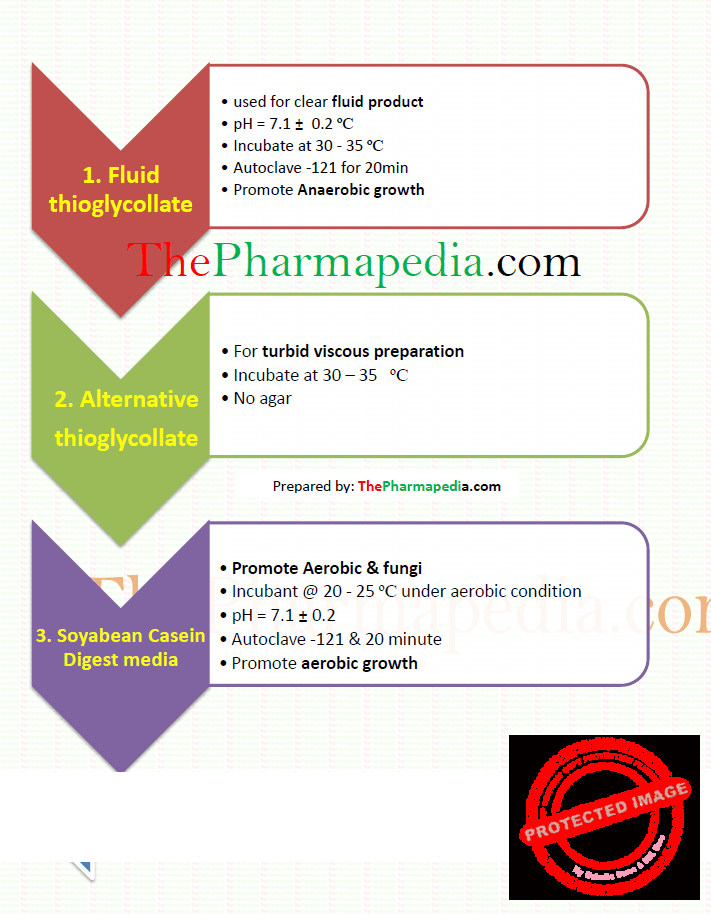
- Fluid Thioglycollate Medium –
-For use with clear fluid products.
-Use fluid thioglycollate medium by incubating it at 30º to 35º.
-Sterilise in an autoclave at 121º for 20 minutes. If the medium is to be stored, cool promptly to 25º and store at 2º to 30º, avoiding excess of light.

2. Alternative Thioglycollate Medium —
For use with turbid and viscid products and for devices having tubes with small lumina.
Sterilize at 121º for 20 minutes. Store at a temperature between 2º and 25º in a sterile sealed container.
incubation at 30º to 35º

3. Soyabean-casein Digest Medium
Sterilise in an autoclave at 121º for 20 minutes.
Use soyabean-casein digest medium by incubating it at 20º to 25º under aerobic conditions.
Soyabean-casein digest medium is suitable for the culture of both fungi and aerobic bacteria.

Test Microorganism for culture media-

Minimum quantity to be used for each medium Sterility Test
| Dosage Form | Quantity per container | Minimum quantity to be used for each medium for sterility test |
|---|---|---|
| For Liquids | less than 1 ml | The whole contents of each container |
| 1-40 ml | Half the contents of each container but not less than 1 ml | |
| Greater than 40 ml and not greater than 100 ml | 20 ml | |
| Greater than 100 ml | 10 percent of the contents of the container but not less than 20 ml | |
| Antibiotic liquids | 1 ml | |
| Insoluble preparations, creams and ointments | Insoluble preparations, creams and ointments | Use the contents of each container to provide not less than 200 mg |
| For Solids | ||
| less than 50 mg | The whole contents of each container | |
| 50 mg or more but less than 300 mg | Half the contents of each container but not less than 50 mg | |
| 300 mg – 5 g | 100 mg(IP) USP-150 mg | |
| Greater than 5 g | 500 mg |
Minimum number of items to be tested for Sterility Test
| Items | Minimum number of items to be tested for each medium for Sterility Test |
|---|---|
| Injectable preparations Not more than 100 containers More than 100 but not more than 500 containers More than 500 containers | 10 percent or 4 containers whichever 10 containers 2 percent or 20 containers s (10 containers for large-volume parenteral) whichever is the less |
| Ophthalmic and other non-injectable preparations Not more than 200 containers More than 200 containers | 5 percent or 2 containers whichever is the greatest 10 containers |
| Surgical dressings Not more than 100 packages More than 100 but not more than 500 packages More than 500 packages | 10 per cent or 4 packages whichever is the greater 10 packages 2 percent or 20 packages whichever is the less |
| Bulk solids Less than 4 containers 4 containers but not more than 50 containers More than 50 containers is the greater | Each container 20 percent or 4 containers whichever is the greater 2 percent or 10 containers whichever |
2. Pyrogen test / Endotoxin Test
‘Lipo’ portion – Responsible for Biological responses i.e. fever
1.LAL Test (Limulus Amebocytes Lysate)
Solution of substances intended for parenteral administration in large volumes (10 ml or more at a time) shall be pyrogen-free and tested for pyrogens. If water or any other aqueous solvent is supplied along with the substances for preparing such solutions, it shall also be pyrogen-free and tested for pyrogens.
–in vitro test
-5 time more sensitive
– Limulus Amebocytes Lysate: LAL test is a simple method for the detection of viable and non-viable Gram-negative bacteria. Gram-negative bacteria produce lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (endotoxin), which is a high-molecular-weight complex; it is generally not produced by Gram-positive bacteria. Lipopolysaccharides (i.e. endotoxins) of this bacterial group lead to gelation of blood cell (amoebocytes) lysates of the Limulus polyphemus crab.
-37 oC For 1 hr [incubation] – Formation of Gel :- (+ve) Result
2. Rabbit test (in vivo)
The test involves measurement of the rise in body temperature of rabbits following the IV injection of a sterile solution into the ear vein of the rabbit. Dose not exceeding 10 ml per kg injected intravenously within a period of not more than 10 mins.
Test animals: Use healthy, adult rabbits of either sex, preferably of the same variety. Recording of temperature: Clinical thermometer, a thermistor.
PRELIMINARY TEST(SHAM TEST)
If animals are used for the first time in a pyrogen test or have not been used during the 2 previous weeks,condition them 1 to 3 days before testing the substance by injecting IV 10ml per kg pyrogen-free saline solution warmed to about 38.5°.
Record the temperature of the animals, beginning at least 90 mins before injection and continuing for 3 hours after injection.
Any animal showing a temperature variation of 0.6° or more must not be used in main test.
Main Test
Carry out the test using a group of 3 rabbits. Preparation of the sample: Dissolve the substance in,or dilute with, pyrogen free saline solution.Warm the liquid to approximately 38.5° before injection.
Interpretation of rabbits test:
| No. of Rabbit | Individual Temp rise not more than oC | Temp rise in group ( oC )not more than | Test Result |
| 3 Rabbit | 0.6 oC | 1.4 oC | Passes |
| Addition 5 Rabbit (total 3 + 5 = 8) | 0.6 oC | 3.7 oC | Passes |
Pyrogen/Endotoxin: Rabbit in-vivo test
3. Monocyte Activation test (New latest test)
It is the new latest test to detect the presence of endotoxin.
3. Isotonicity
- must be isotonic [0.9% w/v of NaCl] (286 m Mol/L – Osmalarity) to body fluids
- Determined by
- Freezing Point depression
- Hemolysis method using RBCs
4. Clearity / Foreign particulate matter test
Parenteral products should free from foreign contamination, particles, debrige etc.
Filter using 0.2 um membrane filter.
5. Leaker Test
- Performed by producing –ve/negative pressure (vaccum) within ampules immersed in dye [methylene Blue-1%] – For Ampules
- For vial/ bottle: Leaker test is performed
- – water hammer sound test
- – Spark tester probe
Also Read….
Formulation of Parenteral Sterile Products/preparation
Containers and Closers for Parenteral Sterile Preparation/Product
Join Our WhatsApp Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to Download Free Books & Notes, Previous papers for D.Pharm, B.Pharm, M.Pharm, Drug Inspector & GPAT……….









Pingback: Evaluation of Ophthalmic preparation | Pharmacy Notes-GPAT Pharmacist Drug Inspector | The Pharmapedia
Pingback: Test for Evaluation of Cream | Pharmacy Notes | The Pharmapedia
Pingback: Containers and Closers for Parenteral Sterile Preparation/Product | The Pharmapedia